

Article Critique
Ai generator.
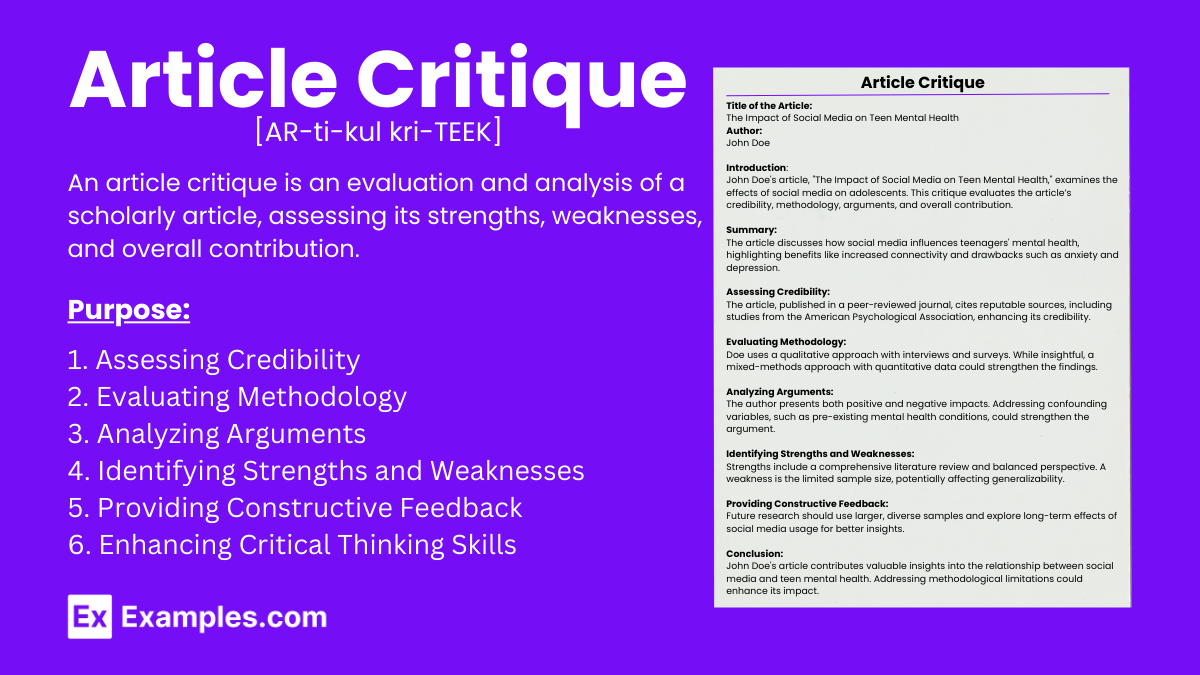
In the realm of academia and intellectual discourse, the art of critiquing articles holds significant importance. It not only refines one’s skills but also contributes to the growth of knowledge. A well-executed article critique showcases your ability to analyze, evaluate, and engage with scholarly work. This article delves into the concept of article critiques, offering insights into their purpose and benefits, along with a step-by-step guide on how to craft one effectively.
What is an Article Critique?
An article critique is a detailed evaluation and analysis of a scholarly article or research paper . It involves an objective assessment of the author’s arguments, evidence, methodology, and conclusions. An effective critique goes beyond summarizing the content; it delves into the strengths, weaknesses, and implications of the article. Developing this skill allows you to identify the characteristics that contribute to a compelling scholarly work, while also honing your ability to engage critically with academic literature.
Article Critique Format
1. introduction.
- Article Information : Mention the title of the article, the author’s name, the source ( journal , magazine , etc.), and the publication date.
- Thesis Statement : Summarize the main argument or purpose of the article.
- Scope of the Critique : Briefly outline the main points you will discuss in your critique.
2. Summary of the Article
- Main Points : Summarize the key points and arguments presented by the author.
- Purpose and Scope : Explain the purpose of the article and the main topics covered.
- Findings and Conclusions : Highlight the primary findings and conclusions drawn by the author.
3. Critical Analysis
A. structure and organization.
- Introduction : Evaluate the effectiveness of the introduction. Does it set the stage for the article?
- Body : Assess the organization of the main sections. Are the arguments and evidence presented logically?
- Conclusion : Examine the conclusion. Does it effectively summarize the article and provide closure?
b. Content and Arguments
- Clarity : Determine if the article is clear and easy to understand.
- Evidence : Analyze the evidence used to support the arguments. Is it relevant and convincing?
- Consistency : Check for logical consistency in the arguments.
c. Research Methodology
- Approach : Evaluate the research methods used in the article. Are they appropriate for the research question ?
- Data Collection : Assess the reliability and validity of the data collection methods.
- Analysis : Examine the thoroughness and accuracy of the data analysis .
d. Writing Style
- Tone : Assess the appropriateness of the tone for the target audience.
- Language : Evaluate the use of language. Is it precise and concise?
- Grammar and Syntax : Check for grammatical correctness and syntactical clarity.
e. Contribution to the Field
- Originality : Determine the originality of the article. Does it offer new insights?
- Impact : Assess the potential impact of the article on the field. Does it advance knowledge or understanding?
4. Personal Response
- Strengths : Identify the strengths of the article. What did the author do well?
- Weaknesses : Point out the weaknesses or areas for improvement.
- Overall Impression : Provide your overall impression of the article.
5. Conclusion
- Summary : Summarize your main points of critique.
- Recommendation : Offer any recommendations for future research or improvements to the article.
6. References
- Citation : Provide a full citation of the article in the appropriate format (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Additional Sources : Include citations for any additional sources referenced in your critique.
Examples of Article Critique For Students
Psychology article critique.
Reference: Smith, J. A., & Brown, R. L. (2022). The impact of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance. Journal of Psychological Research , 34(2), 123-135. https://doi.org/10.1001/jpsychres.2022.01.001 Introduction In their article “The Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Cognitive Performance,” Smith and Brown (2022) examine the effects of sleep deprivation on various cognitive functions. The authors aim to highlight the importance of adequate sleep for maintaining cognitive health and performance. Summary Smith and Brown (2022) conducted a series of cognitive tests on participants who were sleep-deprived for 24 hours. The results indicated significant declines in memory retention, attention span, and problem-solving skills among the sleep-deprived group. The article also discusses potential long-term consequences of chronic sleep deprivation on brain health. Critique Smith and Brown (2022) provide compelling evidence linking sleep deprivation to cognitive decline. Their methodology is robust, featuring a well-defined participant group and controlled variables. However, the study’s sample size is relatively small, which may limit the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, the article does not sufficiently explore potential confounding factors, such as stress and caffeine intake, which could influence cognitive performance. Conclusion Overall, Smith and Brown (2022) effectively underscore the critical role of sleep in cognitive health. Despite some methodological limitations, their findings contribute valuable insights to the field of sleep research. Future studies should aim to address the identified limitations to strengthen the generalizability and applicability of the results.
Education Article Critique
Reference: Johnson, L. M., & White, P. D. (2023). The impact of technology integration on student learning outcomes. Journal of Educational Technology , 29(1), 45-59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeduc.2023.01.002 Introduction In the article “The Impact of Technology Integration on Student Learning Outcomes,” Johnson and White (2023) explore how incorporating digital tools and resources in the classroom affects students’ academic performance. The authors aim to identify both the benefits and challenges of technology integration in education. Summary Johnson and White (2023) evaluate various forms of technology integration, including interactive whiteboards, educational software, and online resources. They analyze the effects of these tools on student engagement, motivation, and achievement across different subjects and grade levels. The study presents data from several schools that have implemented these technologies, showing improvements in test scores and classroom participation. Critique The article by Johnson and White (2023) provides a comprehensive analysis of the positive impacts of technology on student learning. The use of multiple case studies strengthens the validity of their conclusions. However, the study’s focus on urban schools may not reflect the experiences of students in rural or underfunded schools, limiting the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, the reliance on short-term data does not capture the long-term effects of technology integration on student learning. Conclusion Johnson and White (2023) make a compelling case for the positive impact of technology on student learning outcomes. While the article effectively demonstrates the benefits of digital tools, addressing the identified limitations would provide a more comprehensive understanding of technology integration in education. Future research should focus on long-term effects, diverse educational settings, and the challenges of teacher training and equitable access to technology.
Business Article Critique
Reference: Davis, K. L., & Roberts, J. H. (2021). Corporate social responsibility and business success: A review of recent research. Journal of Business Ethics , 38(4), 220-235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbuseth.2021.02.003 Introduction In their article “Corporate Social Responsibility and Business Success: A Review of Recent Research,” Davis and Roberts (2021) explore how corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives impact business performance. The authors aim to demonstrate the benefits of CSR in enhancing corporate reputation and customer loyalty. Summary Davis and Roberts (2021) review several studies that analyze the outcomes of CSR initiatives across different industries. The article highlights positive correlations between CSR activities and financial performance, as well as improvements in brand reputation and customer satisfaction. The authors also discuss the potential challenges businesses face when implementing CSR programs. Critique Davis and Roberts (2021) provide a thorough review of the literature on CSR and its impact on business success. The article effectively synthesizes findings from various studies, supporting their argument that CSR can be beneficial for companies. However, the article could be improved by including more critical perspectives on CSR, such as potential drawbacks or instances where CSR initiatives have failed. Additionally, the authors do not provide detailed guidelines on how companies can measure the effectiveness of their CSR efforts. Conclusion Overall, Davis and Roberts (2021) make a strong case for the positive impact of CSR on business success. Their review underscores the importance of socially responsible practices in building a positive corporate image and achieving long-term profitability. Future research should address the limitations noted, particularly by exploring the challenges and failures of CSR initiatives and providing actionable metrics for evaluating their success.
Health Sciences Article Critique
Reference: Nguyen, M. T., & Kim, H. S. (2020). The effects of a plant-based diet on cardiovascular health: A systematic review. Journal of Nutritional Science , 17(3), 95-110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutrsci.2020.03.005 Introduction In the article “The Effects of a Plant-Based Diet on Cardiovascular Health: A Systematic Review,” Nguyen and Kim (2020) investigate the impact of plant-based diets on heart disease prevention and management. The authors aim to provide evidence supporting dietary recommendations for cardiovascular health. Summary Nguyen and Kim (2020) review multiple studies comparing the cardiovascular outcomes of individuals on plant-based diets versus those on omnivorous diets. Their findings suggest that plant-based diets are associated with lower cholesterol levels, reduced blood pressure, and decreased incidence of heart disease. The authors discuss potential mechanisms, such as reduced intake of saturated fats and increased consumption of fiber and antioxidants. Critique Nguyen and Kim (2020) present a comprehensive review of the cardiovascular benefits of plant-based diets. The inclusion of various studies strengthens the validity of their conclusions. However, the review would benefit from a more balanced discussion of potential challenges, such as the risk of nutrient deficiencies and the social and cultural barriers to adopting a plant-based diet. Additionally, the article focuses primarily on short-term studies, and more research on the long-term sustainability of these diets is needed. Conclusion Overall, Nguyen and Kim (2020) provide strong evidence supporting the cardiovascular benefits of plant-based diets. Their systematic review contributes valuable insights to the field of nutritional science. Future research should address the limitations identified, particularly regarding long-term sustainability and potential challenges in adhering to plant-based diets.
Social Sciences Article Critique
Reference: Lopez, G. R., & Thompson, S. L. (2021). Urban poverty and social policy: Examining the effectiveness of welfare programs. Journal of Social Policy , 43(2), 180-195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2021.04.007 Introduction In the article “Urban Poverty and Social Policy: Examining the Effectiveness of Welfare Programs,” Lopez and Thompson (2021) analyze the impact of various welfare programs on reducing urban poverty. The authors aim to assess the effectiveness of these programs in improving the socioeconomic conditions of urban populations. Summary Lopez and Thompson (2021) evaluate several welfare programs, including food assistance, housing subsidies, and employment training initiatives. Their analysis reveals mixed outcomes, with some programs showing significant positive effects on poverty reduction, while others have minimal impact. The authors discuss factors contributing to these varied results, such as program design, implementation quality, and participant engagement. Critique Lopez and Thompson (2021) provide a detailed analysis of the effectiveness of welfare programs in addressing urban poverty. The article’s strength lies in its comprehensive evaluation of multiple programs and consideration of various influencing factors. However, the study relies on data from a limited number of cities, which may not be representative of broader urban contexts. Additionally, the authors could have included more qualitative data to provide deeper insights into the lived experiences of program participants. Conclusion Overall, Lopez and Thompson (2021) offer valuable insights into the effectiveness of welfare programs in reducing urban poverty. Their findings highlight the need for well-designed and effectively implemented programs to achieve meaningful poverty reduction. Future research should aim to include a more diverse range of urban settings and incorporate qualitative data to enrich the understanding of program impacts.
Examples of Thesis Statements for Article Critiques
Psychology article critique thesis statements.
- “The article successfully links mindfulness practices to reduced anxiety levels, yet it overlooks the potential variability in individual responses, which could affect the generalizability of the results.”
- “While the study provides significant insights into the effects of social media on adolescent self-esteem, its cross-sectional design limits the ability to infer causality.”
Literature Article Critique Thesis Statements
- “The article provides a nuanced analysis of the themes of isolation in ‘Frankenstein,’ but its limited engagement with contemporary critical perspectives reduces its impact.”
- “Although the article offers a compelling interpretation of symbolism in ‘Moby Dick,’ its narrow focus on literary devices neglects the broader socio-political context of the novel.”
Business Article Critique Thesis Statements
- “The article effectively highlights the benefits of agile project management in tech startups, but it fails to consider the potential downsides, such as the risk of scope creep and resource strain.”
- “Despite presenting a well-researched argument for the advantages of remote work, the article’s lack of empirical data on long-term productivity effects weakens its conclusions.”
Health Sciences Article Critique Thesis Statements
- “The article convincingly argues for the role of gut microbiota in mental health, though it would benefit from a more thorough exploration of the mechanisms underlying this relationship.”
- “While the study provides strong evidence for the benefits of intermittent fasting on metabolic health, its reliance on short-term studies limits the understanding of long-term effects.”
Education Article Critique Thesis Statements
- “The article makes a strong case for the use of gamification in education to enhance student motivation, yet it neglects to address potential challenges related to accessibility and equity.”
- “Despite effectively demonstrating the positive impacts of project-based learning on student engagement, the article lacks consideration of the additional resources and training required for successful implementation.”
Environmental Science Article Critique Thesis Statements
- “The article offers a comprehensive review of the impacts of deforestation on climate change, but it would be strengthened by incorporating more case studies from diverse geographic regions.”
- “While the article effectively discusses the potential of urban green spaces to mitigate air pollution, it underestimates the complexities of urban planning and maintenance costs.”
Social Sciences Article Critique Thesis Statements
- “The article provides valuable insights into the influence of cultural norms on gender roles, but its limited geographic focus restricts the applicability of its findings to a global context.”
- “Although the study sheds light on the relationship between economic inequality and crime rates, its reliance on correlational data makes it difficult to draw definitive causal conclusions.”
Example of Article Critique About Education
Article Title : The Impact of Technology Integration on Student Learning Outcomes Introduction The article “The Impact of Technology Integration on Student Learning Outcomes” investigates how the use of digital tools and resources in the classroom influences students’ academic performance. The research aims to identify the benefits and potential drawbacks of incorporating technology into educational settings. Summary The study evaluates various forms of technology integration, including interactive whiteboards, educational software, and online resources. It examines their effects on student engagement, motivation, and achievement across different subjects and grade levels. The article presents data from several schools that have implemented these technologies, showcasing improvements in test scores and classroom participation. Critique The article provides a comprehensive analysis of the positive impacts of technology on student learning. The use of multiple case studies strengthens the validity of its conclusions. However, the article could improve by addressing some critical aspects: Sample Size and Diversity : The study primarily focuses on schools in urban areas, which may not reflect the experiences of students in rural or underfunded schools. Expanding the sample size to include a more diverse range of schools would enhance the generalizability of the findings. Longitudinal Data : The research relies heavily on short-term data, which may not capture the long-term effects of technology integration on student learning. Longitudinal studies are necessary to understand the sustained impact of these tools. Teacher Training and Support : While the article highlights the benefits of technology, it overlooks the challenges teachers face in integrating these tools effectively. Providing adequate training and ongoing support is crucial for the successful implementation of technology in the classroom. Equity and Access : The article briefly mentions the digital divide but does not delve into how disparities in access to technology can affect educational outcomes. A more thorough examination of equity issues would provide a balanced perspective on the advantages and limitations of technology integration. Conclusion Overall, the article makes a compelling case for the positive impact of technology on student learning outcomes. It effectively demonstrates how digital tools can enhance engagement and academic performance. However, to provide a more comprehensive understanding, future research should address the limitations identified, particularly regarding sample diversity, long-term effects, teacher support, and equity issues. By doing so, the research could offer more actionable insights for policymakers and educators striving to harness the full potential of technology in education.
More Examples & Samples Article Critique in PDF
1. quantitative article critique.

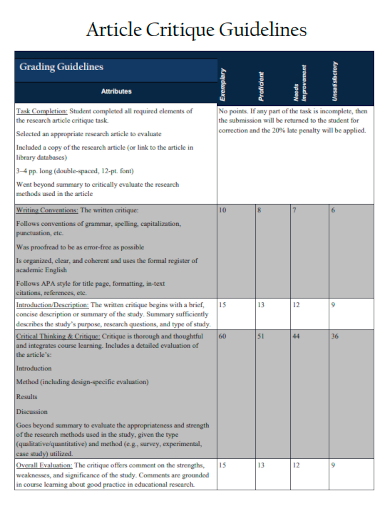
2. Article Critique Guidelines
4. Critiquing Research Articles

4. Article Review & Critiques

5. Instructions for Article Critiques

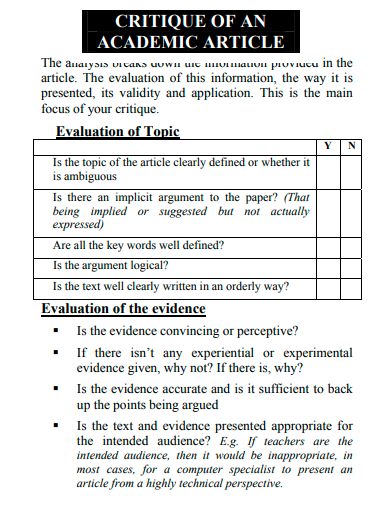
6. Critique of an Academic Article
7. Critique and Review of Research Articles

8. Article Critique Assignment

9. Book Review or Article Critique

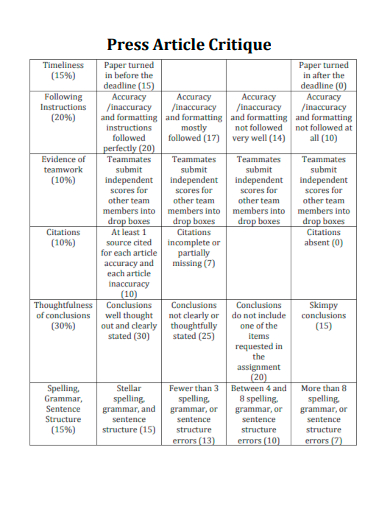
10. Press Article Critique
Purpose of Article Critique
An article critique serves multiple essential purposes in both academic and professional contexts. Below, we delve into the primary objectives of conducting an article critique, which are vital for developing critical thinking, analytical skills, and subject-specific knowledge.

1. Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Critical Evaluation:
- Encourages students and professionals to go beyond surface-level reading.
- Promotes a deeper understanding of the material by questioning the validity and reliability of the arguments presented.
Analytical Reasoning:
- Helps in identifying logical fallacies, biases, and unsupported claims.
- Facilitates the assessment of evidence and methodologies used in the article.
2. Enhancing Understanding of Subject Matter
In-Depth Analysis:
- Requires a thorough examination of the article’s content, including the main arguments, evidence, and conclusions.
- Enhances comprehension of complex concepts and theories within a specific field.
Contextual Awareness:
- Places the article within the broader context of existing literature.
- Identifies gaps in the research and suggests areas for further investigation.
3. Improving Academic Writing Skills
Structured Writing:
- Teaches students how to organize their thoughts coherently.
- Develops skills in writing clear, concise, and structured critiques.
Evidence-Based Arguments:
- Encourages the use of evidence to support evaluations and opinions.
- Helps in the practice of citing sources correctly and ethically.
4. Facilitating Peer Review and Feedback
Constructive Criticism:
- Provides a framework for giving and receiving constructive feedback.
- Enhances collaborative learning by engaging in discussions about the strengths and weaknesses of an article.
Quality Assurance:
- Plays a crucial role in academic publishing and professional fields by ensuring the quality and credibility of published work.
- Helps maintain high standards in research and scholarship.
5. Encouraging Lifelong Learning
Continual Improvement:
- Fosters a habit of continuous learning and improvement.
- Keeps individuals updated with the latest research, trends, and advancements in their field.
Adaptability:
- Prepares students and professionals to adapt to new information and changing paradigms.
- Cultivates a mindset that is open to questioning and re-evaluating established knowledge.
Components of an Article Critique
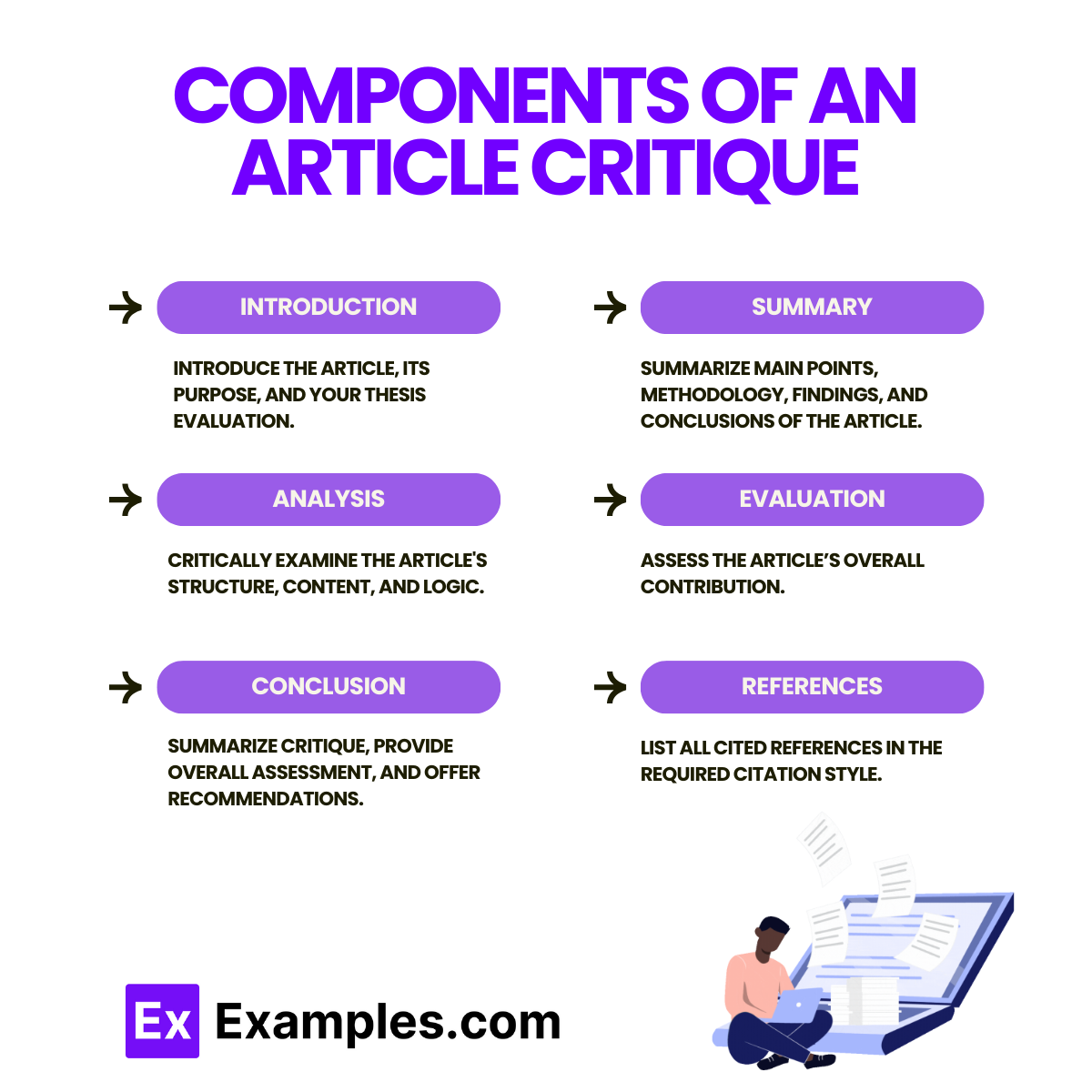
An effective article critique includes several key components to ensure a thorough evaluation and analysis. Below are the main components:
- Provide an overview of the article.
- Introduce the main thesis and key points.
Components:
- Title and Author: State the article’s title and author.
- Publication Details: Include publication name, date, etc.
- Thesis Statement: Summarize the article’s main argument.
- Purpose of the Critique: Explain your objective.
- Summarize the article’s content.
- Main Points: Highlight key arguments.
- Methodology: Describe research methods briefly.
- Findings and Conclusions: Outline main findings and conclusions.
3. Analysis
- Critically examine the article’s structure, content, and logic.
- Structure and Organization: Evaluate clarity and coherence.
- Content Evaluation: Assess relevance and depth.
- Argumentation: Analyze logical flow and evidence strength.
- Methodology: Critique research methods and identify biases.
- Sources and References: Evaluate quality and relevance of cited sources.
4. Evaluation
- Assess the article’s overall contribution.
- Strengths: Highlight strengths such as originality and depth.
- Weaknesses: Identify weaknesses like gaps and biases.
- Contribution to the Field: Discuss the article’s impact.
- Summarize the critique and provide final thoughts.
- Summary of Evaluation: Recap key points.
- Overall Assessment: Provide a final judgment.
- Recommendations: Suggest future research or improvements.
- List sources cited in your critique.
- Citations: Format according to the appropriate style (e.g., APA, MLA).
How to Write an Article Critique
Mastering the art of crafting an effective article critique requires a systematic approach. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you navigate this process with finesse.
Step 1: Reading and Observation
Before diving into the critique, thoroughly read the article. Take notes on the main points, observation , objectives , and tone of the article. Identify the author’s goals and the case study , if applicable. This step is crucial for grasping the nuances of the work.
Step 2: Analyzing Structure and Content
Evaluate the structure of the article. Identify the introduction, main arguments, supporting evidence, and conclusion. Examine the use of verbs and analogies , as well as the cause-and-effect relationships presented. Analyze how effectively the author communicates their ideas.
Step 3: Assessing Methodology and Evidence
Scrutinize the methodology used by the author. Is it appropriate for the objectives of the article? Evaluate the quality and relevance of the evidence presented. Consider whether the evidence supports the author’s claims adequately.
Step 4: Critical Evaluation
Engage in a critical evaluation of the article. Identify its strengths and weaknesses. Does the author effectively address counterarguments? Are there any gaps in the logic? Assess the overall coherence and effectiveness of the article’s presentation.
Why is article critique important?
It develops critical thinking, enhances understanding of the subject, improves academic writing skills, and provides constructive feedback.
What are the main components of an article critique?
Introduction, Summary, Analysis, Evaluation, Conclusion, and References.
How do I start an article critique?
Begin with an introduction that provides the article’s title, author, publication details, and a brief summary of its thesis and purpose.
What should be included in the summary?
Key points, research methods, findings, and conclusions of the article.
How do I analyze an article?
Examine the structure, content, logic, argumentation, methodology, and sources for clarity, relevance, and evidence strength.
What makes a good evaluation?
Balanced assessment of the article’s strengths and weaknesses, and its contribution to the field.
How should I conclude an article critique?
Summarize your findings, provide an overall assessment, and offer suggestions for improvement or future research.
How do I cite sources in an article critique?
Follow the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA) and ensure all references are correctly formatted.
What are common pitfalls to avoid in an article critique?
Avoid biased or overly negative reviews, lack of evidence for claims, and failure to provide a balanced perspective.
How can I ensure my critique is objective?
Use evidence to support your points, acknowledge both strengths and weaknesses, and avoid personal biases.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

Journal Article Critique Guide and Example in 2025.
Journal article critiques are essential tools in academic and professional fields, providing a structured method to analyze and evaluate scholarly work. As we move into 2025, the importance of critical analysis in an age of information overload has only increased. This guide will walk you through the process of crafting a comprehensive journal article critique, highlighting key components and offering practical tips for success.
A journal article critique goes beyond mere summarization, delving into the strengths and weaknesses of the research presented. It requires a careful examination of the article’s methodology, findings, and conclusions, all while considering its relevance and contribution to the field. By mastering the art of critique, you’ll develop crucial skills in critical thinking, analytical writing, and scholarly discourse.
In this Journal Article Critique Guide. we’ll explore the step-by-step process of creating a journal article critique, from initial reading strategies to final presentation. We’ll also provide a detailed example to illustrate these concepts in action, ensuring you have a clear understanding of how to apply these principles to your own work.

What You'll Learn
Understanding the Purpose and Structure of a Journal Article Critique
The primary purpose of a journal article critique is to provide a balanced and objective evaluation of a scholarly work. This evaluation serves multiple functions in the academic community:
- Quality control: Critiques help maintain high standards in research by identifying strengths and weaknesses in published work.
- Knowledge advancement: By analyzing existing research, critiques contribute to the ongoing dialogue within a field and can inspire new avenues of inquiry.
- Skill development: Writing critiques hones critical thinking, analytical, and communication skills essential for academics and professionals.
A well-structured journal article critique typically includes the following components:
- Introduction: Provides an overview of the article and your main assessment.
- Summary: Concisely presents the key points of the original article.
- Critique: Offers a detailed analysis of the article’s strengths and weaknesses.
- Conclusion: Summarizes your overall evaluation and the article’s significance.
Understanding this structure is crucial for organizing your thoughts and presenting a coherent critique. Each section builds upon the previous one, guiding the reader through your analysis and supporting your final assessment.
As we move into 2025, the ability to critically evaluate research has become increasingly important. With the rapid dissemination of information and the growing interdisciplinary nature of many fields, a well-crafted critique can serve as a valuable resource for researchers, students, and professionals alike.
Preparing to Write: Initial Reading and Note-Taking Strategies
Before diving into the critique itself, it’s essential to approach the journal article with a strategic reading and note-taking process. This preparation phase sets the foundation for a thorough and insightful critique.
First Reading: Begin with a quick, overall read of the article to grasp its main ideas and structure. Pay attention to the abstract, introduction, headings, and conclusion. This initial pass helps you understand the article’s general argument and methodology without getting bogged down in details.
Second Reading: During your second, more careful reading, focus on the following elements:
- Research question or hypothesis
- Methodology and data collection
- Results and analysis
- Conclusions and implications
- References and citations
As you read, take detailed notes on each of these aspects. Use a system that works for you, whether it’s digital note-taking tools, handwritten notes, or a combination of both. Consider using a template or table to organize your observations systematically.
Critical Questions: While reading, ask yourself critical questions such as:
- Is the research question clearly stated and relevant?
- Does the methodology appropriately address the research question?
- Are the results presented clearly and interpreted accurately?
- Do the conclusions logically follow from the results?
- Is the article well-organized and clearly written?
By 2025, advanced AI-powered tools may be available to assist in this process, potentially offering automated summaries or highlighting key points. However, developing your own critical reading skills remains crucial for producing insightful critiques.
Analyzing the Article’s Content and Methodology
Once you’ve thoroughly read and taken notes on the article, it’s time to delve deeper into your analysis. This section of your critique should focus on evaluating the content and methodology of the research.
Content Analysis: Examine the article’s arguments, evidence, and theoretical framework. Consider the following:
- Clarity and coherence of the main argument
- Quality and relevance of evidence presented
- Logical flow of ideas and reasoning
- Appropriate use of relevant literature and theories
- Identification and addressing of potential counterarguments
Methodology Evaluation: Assess the research design and methods used in the study:
- Appropriateness of the chosen methodology for the research question
- Sample size and selection process (if applicable)
- Data collection techniques and their potential limitations
- Validity and reliability of measurements or instruments used
- Ethical considerations in the research process
Data Analysis and Interpretation: Scrutinize how the authors analyzed their data and interpreted the results:
- Suitability of statistical tests or qualitative analysis methods
- Clarity and accuracy of data presentation (tables, graphs, etc.)
- Thoroughness of the analysis in addressing all aspects of the research question
- Consideration of alternative explanations for the findings
- Acknowledgment of limitations in the study design or results
As you analyze these elements, remember to balance criticism with recognition of the article’s strengths. A fair and balanced critique acknowledges both the positive aspects and areas for improvement in the research.
Evaluating the Article’s Contribution to the Field
An essential aspect of your critique is assessing the article’s overall contribution to its field of study. This evaluation helps contextualize the research within the broader academic landscape and highlights its significance.
Relevance and Originality: Consider how the article advances knowledge in its area:
- Does it address a gap in existing literature?
- Does it challenge or confirm previous findings?
- Does it introduce new concepts, methodologies, or theoretical frameworks?
- How does it build upon or diverge from established research in the field?
Practical and Theoretical Implications: Examine the potential impact of the research:
- What are the practical applications of the findings?
- How might the results influence future research directions?
- Does the study have implications for policy or practice in its field?
- Are there potential interdisciplinary connections or applications?
Comparison with Similar Research: Place the article in context with related studies:
- How does this research compare to similar studies in terms of methodology and findings?
- Does it offer any unique perspectives or insights?
- Are there any contradictions with established research that need to be addressed?
Long-term Significance: Consider the lasting impact of the research:
- Is the topic likely to remain relevant in the coming years?
- Does the article lay groundwork for future studies?
- How might technological advancements or societal changes affect the relevance of this research?
By thoroughly evaluating these aspects, you can provide a comprehensive assessment of the article’s contribution and significance within its field. This analysis not only adds depth to your critique but also demonstrates your understanding of the broader academic context.
Crafting Your Critique: Writing Tips and Best Practices
Now that you’ve thoroughly analyzed the article, it’s time to translate your insights into a well-structured critique. Follow these writing tips and best practices to ensure your critique is clear, comprehensive, and professional.
Organization:
- Follow the standard structure: introduction, summary, critique, and conclusion.
- Use clear headings and subheadings to guide your reader through each section.
- Ensure a logical flow of ideas within and between paragraphs.
Tone and Style:
- Maintain an objective and scholarly tone throughout your critique.
- Use precise language and avoid unnecessary jargon.
- Strike a balance between formal academic writing and accessibility.
Supporting Your Arguments:
- Provide specific examples from the article to support your points.
- Use direct quotes sparingly and always cite them properly.
- Reference relevant literature to contextualize your critique.
Balancing Criticism and Praise:
- Acknowledge the article’s strengths as well as its weaknesses.
- Offer constructive criticism rather than merely pointing out flaws.
- Provide suggestions for improvement or future research directions.
Clarity and Concision:
- Be clear and direct in your assessments.
- Avoid repetition and unnecessary elaboration.
- Use transition sentences to connect different points and sections.
Proofreading and Editing:
- Review your critique for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
- Ensure consistency in formatting and citation style.
- Consider having a peer review your critique for additional feedback.
By following these guidelines, you’ll create a polished and professional critique that effectively communicates your analysis. Remember, the goal is to provide a fair and insightful evaluation that contributes to the academic discourse surrounding the article’s topic.
Example: A Sample Journal Article Critique
To illustrate the principles discussed in this guide, let’s examine a sample critique of a hypothetical journal article titled “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Workplace Dynamics in 2025” by J. Smith and A. Lee, published in the Journal of Future Work Studies.
Introduction: This critique evaluates Smith and Lee’s (2025) article on the influence of AI in contemporary workplaces. The study provides valuable insights into the changing nature of work but has some methodological limitations that warrant discussion.
Summary: Smith and Lee conducted a mixed-methods study involving surveys of 500 employees across various industries and in-depth interviews with 50 managers. They argue that AI integration in workplaces has led to significant shifts in job roles, skill requirements, and organizational structures. Key findings include:
- 60% of surveyed employees reported changes in their job responsibilities due to AI implementation.
- Managers identified critical thinking and AI literacy as essential skills for future workforce.
- Organizations are increasingly adopting flatter structures to facilitate human-AI collaboration.
Critique: Strengths:
- Timely and relevant topic addressing a critical aspect of modern work environments.
- Comprehensive mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative data with qualitative insights.
- Clear presentation of findings with well-designed graphs and tables.
Weaknesses:
- Limited sample size for the qualitative component may not capture the full range of managerial perspectives.
- Potential selection bias in the survey sample, with a skew towards tech-savvy respondents.
- Lack of longitudinal data to support claims about long-term trends.
The authors provide a compelling argument for the transformative impact of AI on workplace dynamics. However, their conclusions could be strengthened by addressing the limitations in their methodology and considering alternative explanations for their findings.
Conclusion: Despite its limitations, this study offers valuable insights into the evolving relationship between AI and human workers. It lays a foundation for future research and has important implications for workforce development and organizational planning in the AI era.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Journal Article Critiques
When writing a journal article critique, be aware of these common pitfalls that can diminish the quality and effectiveness of your analysis:
- Summarizing without critiquing: While a summary is important, the bulk of your critique should focus on analysis and evaluation. Avoid simply restating the article’s content without offering your own insights.
- Personal bias: Maintain objectivity in your critique. Don’t let your personal opinions or preconceptions about the topic unduly influence your evaluation of the research.
- Nitpicking: Focus on significant aspects of the article rather than minor issues. Critiquing every small detail can detract from your main arguments.
- Lack of balance: Avoid focusing solely on either strengths or weaknesses. A good critique acknowledges both positive aspects and areas for improvement.
- Unsupported claims: Always provide evidence or reasoning to support your critiques. Avoid making broad statements without backing them up.
- Misunderstanding the article: Ensure you fully understand the article’s content and methodology before critiquing it. Misinterpretations can lead to irrelevant or inaccurate criticisms.
- Ignoring context: Consider the article within its broader academic and historical context. Don’t critique it based on current knowledge if it was groundbreaking at the time of publication.
- Overreliance on direct quotes: While quotes can be useful, overusing them can make your critique seem unoriginal. Paraphrase and synthesize information where appropriate.
- Lack of structure: Organize your critique logically. A disorganized critique can be confusing and less impactful.
- Offering vague suggestions: When proposing improvements or future research directions, be as specific as possible. Vague suggestions add little value to your critique.
By avoiding these pitfalls, you can ensure that your critique is focused, balanced, and contributes meaningfully to the academic discourse surrounding the article’s topic.
The Future of Journal Article Critiques: Trends and Technologies
As we look ahead to 2025 and beyond, several trends and technologies are shaping the landscape of journal article critiques:
- AI-assisted analysis: Advanced AI tools are emerging to help researchers identify patterns, inconsistencies, and potential biases in academic articles. These tools can complement human analysis, offering additional insights and saving time.
- Interactive critiques: Digital platforms are enabling more dynamic and interactive forms of critique. Readers can engage with critiques through comments, annotations, and real-time discussions, fostering a more collaborative approach to academic discourse.
- Data visualization: As research becomes increasingly data-driven, critiques are incorporating more sophisticated data visualization techniques to illustrate key points and analyses.
- Open peer review: There’s a growing trend towards transparency in the peer review process. This may influence how critiques are written and shared, with a focus on constructive feedback and open dialogue.
- Interdisciplinary approaches: As research becomes more interdisciplinary, critiques are increasingly drawing on diverse fields of knowledge to provide comprehensive evaluations.
- Emphasis on reproducibility: With the replication crisis in various fields, critiques are placing greater emphasis on evaluating the reproducibility of research findings.
- Real-time updates: In fast-moving fields, critiques may need to be updated as new information emerges. Dynamic publishing platforms could allow for ongoing refinement of critiques.
- Accessibility and inclusivity: There’s a growing focus on making academic discourse more accessible to diverse audiences, which may influence the language and format of critiques.
- Ethical considerations: As research tackles more complex and sensitive topics, critiques are paying increased attention to the ethical implications of studies.
- Integration with systematic reviews: Critiques may become more closely linked with systematic review processes, contributing to broader syntheses of research in particular fields.
Related Article: Literature Topics and Research
FAQs on Journal Article Critique Guide
How do you write a journal critique?
To write a journal critique, start by thoroughly reading the article and taking notes. Then, structure your critique with an introduction, summary, detailed analysis of strengths and weaknesses, and a conclusion. Focus on evaluating the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions. Provide evidence for your assessments and maintain an objective tone throughout.
What are some examples of critiques?
Examples of critiques include book reviews, film critiques, art criticism, and academic peer reviews. In an academic context, journal article critiques, literature reviews, and research proposal evaluations are common forms of critique.
How to write a critique example?
To write a critique example, choose a specific article or work to analyze. Follow the structure outlined in this guide: introduce the work, summarize its main points, provide a detailed analysis of its strengths and weaknesses, and conclude with your overall assessment. Use specific examples from the work to support your points.
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Post navigation
Previous post.
📕 Studying HQ
Typically replies within minutes
Hey! 👋 Need help with an assignment?
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us
- All eBooks & Audiobooks
- Academic eBook Collection
- Home Grown eBook Collection
- Off-Campus Access
- Literature Resource Center
- Opposing Viewpoints
- ProQuest Central
- Course Guides
- Citing Sources
- Library Research
- Websites by Topic
- Book-a-Librarian
- Research Tutorials
- Use the Catalog
- Use Databases
- Use Films on Demand
- Use Home Grown eBooks
- Use NC LIVE
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary vs. Secondary
- Scholarly vs. Popular
- Make an Appointment
- Writing Tools
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing Center
Service Alert

Article Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing an article SUMMARY
- Writing an article REVIEW
Writing an article CRITIQUE
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- About RCC Library
Text: 336-308-8801
Email: [email protected]
Call: 336-633-0204
Schedule: Book-a-Librarian
Like us on Facebook
Links on this guide may go to external web sites not connected with Randolph Community College. Their inclusion is not an endorsement by Randolph Community College and the College is not responsible for the accuracy of their content or the security of their site.
A critique asks you to evaluate an article and the author’s argument. You will need to look critically at what the author is claiming, evaluate the research methods, and look for possible problems with, or applications of, the researcher’s claims.
Introduction
Give an overview of the author’s main points and how the author supports those points. Explain what the author found and describe the process they used to arrive at this conclusion.
Body Paragraphs
Interpret the information from the article:
- Does the author review previous studies? Is current and relevant research used?
- What type of research was used – empirical studies, anecdotal material, or personal observations?
- Was the sample too small to generalize from?
- Was the participant group lacking in diversity (race, gender, age, education, socioeconomic status, etc.)
- For instance, volunteers gathered at a health food store might have different attitudes about nutrition than the population at large.
- How useful does this work seem to you? How does the author suggest the findings could be applied and how do you believe they could be applied?
- How could the study have been improved in your opinion?
- Does the author appear to have any biases (related to gender, race, class, or politics)?
- Is the writing clear and easy to follow? Does the author’s tone add to or detract from the article?
- How useful are the visuals (such as tables, charts, maps, photographs) included, if any? How do they help to illustrate the argument? Are they confusing or hard to read?
- What further research might be conducted on this subject?
Try to synthesize the pieces of your critique to emphasize your own main points about the author’s work, relating the researcher’s work to your own knowledge or to topics being discussed in your course.
From the Center for Academic Excellence (opens in a new window), University of Saint Joseph Connecticut
Additional Resources
All links open in a new window.
Writing an Article Critique (from The University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center)
How to Critique an Article (from Essaypro.com)
How to Write an Article Critique (from EliteEditing.com.au)
- << Previous: Writing an article REVIEW
- Next: Citing Sources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 9:32 AM
- URL: https://libguides.randolph.edu/summaries

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
questionable!decision!making!on!alower!level.!Udo!Pesch!sees!this!as!"undesirable"!and!writes! thatby!carrying!outthe!policies!the!public!administrator!is!at ...
An article critique requires you to critically read a piece of research and identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the article. ... A summary of a research article requires you to share the key points of the article so your reader can get a ... relevancy, and accuracy of the article, using specific examples from the article to ...
Critical review of the predictibility, causality and falsifiability of two theories of the attitude-behavior relationship: The theory of reasoned action and the theory of planned behaviour ...
What is an Article Critique? An article critique is a detailed evaluation and analysis of a scholarly article or research paper. It involves an objective assessment of the author's arguments, evidence, methodology, and conclusions. An effective critique goes beyond summarizing the content; it delves into the strengths, weaknesses, and ...
If you are asked to write a critique of a research article, you should focus on these issues. You will also need to consider where and when the article was published and who wrote it. This handout presents guidelines for writing a research critique and questions to consider in writing a critique. 1 Taylor, G. (2009).
Examples of critiques include book reviews, film critiques, art criticism, and academic peer reviews. In an academic context, journal article critiques, literature reviews, and research proposal evaluations are common forms of critique. How to write a critique example? To write a critique example, choose a specific article or work to analyze.
An article critique will require you to critically read a piece of research and identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the article. How is a critique different from a summary? A summary of a research article requires you to share the key points of the article so your reader can get a clear picture of what the article is about. A ...
Coming back to the research article critique,try to study the problem and see if the author makes some statement. Then, focus on review of the relevant literature, and hypothesis or research questions set by the author. ... Below is the short passage, an article critique sample that will help you get an idea of how it's done:
of the article and the supporting points that the article uses. o 3 Read the article again. To write a thorough article critique you must have thorough knowledge of the article. Reading it more than once helps to ensure that you haven't missed any important details. o 4 Consider the credentials of the author. Does the author of the article
A critique asks you to evaluate an article and the author's argument. You will need to look critically at what the author is claiming, evaluate the research methods, and look for possible problems with, or applications of, the researcher's claims.