

What is a case report study?
What is a Case Report Study?
A case report study is a type of clinical research that involves the detailed description of a single patient or a small number of patients with a specific disease, condition, or treatment. It is a written account of a patient’s medical history, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and outcome, with the aim of providing a comprehensive understanding of the case. Case reports are often published in medical journals and are considered an important tool for medical professionals, researchers, and patients seeking to learn more about a particular condition or treatment.
Why Use Case Report Studies?
There are several reasons why case report studies are valuable in medical research:
• Unique and Rare Cases : Case report studies provide an opportunity to document unusual or rare cases that may not be captured by larger, more generalizable studies. • Illustrate Complex Issues : Case reports can highlight complex issues or unusual presentations of a disease, making it easier for healthcare providers to understand and recognize similar cases in the future. • Educate and Inform : Case reports can serve as a teaching tool, helping to educate healthcare providers about a particular condition or treatment. • Contribute to Knowledge Base : Case reports can contribute to the existing body of knowledge about a particular disease or condition, helping to advance research and improve patient care.
What is Typically Included in a Case Report Study?
A typical case report study includes the following elements:
- Patient Demographics : The patient’s age, gender, and other relevant demographic information.
- Medical History : A detailed account of the patient’s medical history, including previous illnesses, surgeries, and treatments.
- Problem/Admission : A description of the patient’s symptoms, complaints, or reasons for admission to the hospital or healthcare facility.
- Examination and Diagnosis : A detailed description of the patient’s examination (including physical and laboratory tests) and the diagnosis made by the healthcare provider(s).
- Treatment and Management : A description of the treatment and management plan, including medications, procedures, and other interventions.
- Outcome : A report of the patient’s outcome, including any complications, hospital course, and discharge or follow-up information.
Types of Case Report Studies
There are several types of case report studies, including:
- Descriptive Case Reports : A detailed description of a single patient or a small number of patients with a specific disease or condition.
- Exploratory Case Reports : An in-depth examination of a small number of patients with a rare or unusual condition.
- Analytical Case Reports : A quantitative analysis of a small number of patients with a specific condition, including statistical analysis and comparison with larger studies.
- Narrative Case Reports : A narrative account of a patient’s experience, focusing on the patient’s perspective and story.
Importance of Case Report Studies in Medicine
Case report studies play a significant role in medicine, particularly in the following areas:
- Raising Awareness : Case reports can raise awareness about a particular condition or treatment, helping to promote early recognition and intervention.
- Advancing Therapeutic Options : Case reports can identify new and effective treatment approaches, contributing to the development of new therapeutic options.
- Improving Patient Care : Case reports can help improve patient care by providing healthcare providers with more information about a particular condition or treatment.
In conclusion, case report studies are an important tool in medical research, providing valuable insights into unique and rare cases that may not be captured by larger studies. By publishing case reports, healthcare providers and researchers can advance our understanding of a particular condition or treatment, leading to improved patient care and outcomes. Whether used to raise awareness, advance therapeutic options, or improve patient care, case report studies play a significant role in the field of medicine.
- How to price a saas product?
- How to download YouTube audio to mac?
- Are online teaching degrees respected?
- How to change Apple Music name?
- How to clean Apple watch ultra bands?
- How to see the full card number on Apple Pay?
- How to turn off AI on Snapchat?
- Do high school grades matter in college?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Fundamentals of case study research in family medicine and community health
Author affiliations
Michael D Fetters 2
The aim of this article is to introduce family medicine researchers to case study research, a rigorous research methodology commonly used in the social and health sciences and only distantly related to clinical case reports. The article begins with an overview of case study in the social and health sciences, including its definition, potential applications, historical background and core features. This is followed by a 10-step description of the process of conducting a case study project illustrated using a case study conducted about a teaching programme executed to teach international family medicine resident learners sensitive examination skills. Steps for conducting a case study include (1) conducting a literature review; (2) formulating the research questions; (3) ensuring that a case study is appropriate; (4) determining the type of case study design; (5) defining boundaries of the case(s) and selecting the case(s); (6) preparing for data collection; (7) collecting and organising the data; (8) analysing the data; (9) writing the case study report; and (10) appraising the quality. Case study research is a highly flexible and powerful research tool available to family medicine researchers for a variety of applications.
- Significance statement
Given their potential for answering ‘how’ and ‘why’ questions about complex issues in their natural setting, case study designs are being increasingly used in the health sciences. Conducting a case study can, however, be a complex task because of the possibility of combining multiple methods and the need to choose between different types of case study designs. In order to introduce family medicine and community health researchers to the fundamentals of case study research, this article reviews its definition, potential applications, historical background and main characteristics. It follows on with a practical, step-by-step description of the case study process that will be useful to researchers interested in implementing this research design in their own practice.
- Introduction
This article provides family medicine and community health researchers a concise resource to conduct case study research. The article opens with an overview of case study in the social and health sciences, including its definition, potential applications, historical background and core features. This is followed by a 10-step description of the process of conducting a case study project, as described in the literature. These steps are illustrated using a case study about a teaching programme executed to teach international medical learners sensitive examination skills. The article ends with recommendations of useful articles and textbooks on case study research.
- Origins of case study research
Case study is a research design that involves an intensive and holistic examination of a contemporary phenomenon in a real-life setting. 1–3 It uses a variety of methods and multiple data sources to explore, describe or explain a single case bounded in time and place (ie, an event, individual, group, organisation or programme). A distinctive feature of case study is its focus on the particular characteristics of the case being studied and the contextual aspects, relationships and processes influencing it. 4 Here we do not include clinical case reports as these are beyond the scope of this article. While distantly related to clinical case reports commonly used to report unusual clinical case presentations or findings, case study is a research approach that is frequently used in the social sciences and health sciences. In contrast to other research designs, such as surveys or experiments, a key strength of case study is that it allows the researcher to adopt a holistic approach—rather than an isolated approach—to the study of social phenomena. As argued by Yin, 3 case studies are particularly suitable for answering ‘how’ research questions (ie, how a treatment was received) as well as ‘why’ research questions (ie, why the treatment produced the observed outcomes).
Given its potential for understanding complex processes as they occur in their natural setting, case study increasingly is used in a wide range of health-related disciplines and fields, including medicine, 5 nursing, 6 health services research 1 and health communication. 7 With regard to clinical practice and research, a number of authors 1 5 8 have highlighted how insights gained from case study designs can be used to describe patients’ experiences regarding care, explore health professionals’ perceptions regarding a policy change, and understand why medical treatments and complex interventions succeed or fail.
In anthropology and sociology, case study as a research design was introduced as a response to the prevailing view of quantitative research as the primary way of undertaking research. 9 From its beginnings, social scientists saw case study as a method to obtain comprehensive accounts of social phenomena from participants. In addition, it could complement the findings of survey research. Between the 1920s and 1960s, case study became the predominant research approach among the members of the Department of Sociology of the University of Chicago, widely known as ‘The Chicago School’. 10 11 During this period, prominent sociologists, such as Florian Znaniecki, William Thomas, Everett C Hughes and Howard S Becker, undertook a series of innovative case studies (including classical works such as The Polish peasant in Europe and America or Boys in White ), which laid the foundations of case study designs as implemented today.
In the 1970s, case study increasingly was adopted in the USA and UK in applied disciplines and fields, such as education, programme evaluation and public policy research. 12 As a response to the limitations of quasi-experimental designs for undertaking comprehensive programme evaluations, researchers in these disciplines saw in case studies—either alone or in combination with experimental designs—an opportunity to gain additional insights into the outcomes of programme implementation. In the mid-1980s and early 1990s, the case study approach became recognised as having its own ‘logic of design’ (p46). 13 This period coincides with the publication of a considerable number of influential articles 14–16 and textbooks 4 17 18 on case study research.
These publications were instrumental in shaping contemporary case study practice, yet they reflected divergent views about the nature of case study, including how it should be defined, designed and implemented (see Yazan 19 for a comparison of the perspectives of Yin, Merriam and Stake, three leading case study methodologists). What these publications have in common is that case study revolves around four key features.
First, case study examines a specific phenomenon in detail by performing an indepth and intensive analysis of the selected case. The rationale for case study designs, rather than more expansive designs such as surveys, is that the researcher is interested in investigating the particularity of a case, that is, the unique attributes that define an event, individual, group, organisation or programme. 2 Second, case study is conducted in natural settings where people meet, interact and change their perceptions over time. The use of the case study design is a choice in favour of ‘maintaining the naturalness of the research situation and the natural course of events’ (p177). 20
Third, case study assumes that a case under investigation is entangled with the context in which it is embedded. This context entails a number of interconnected processes that cannot be disassociated from the case, but rather are part of the study. The case study researcher is interested in understanding how and why such processes take place and, consequently, uncovering the interactions between a case and its context. Research questions concerning how and why phenomena occur are particularly appropriate in case study research. 3
Fourth, case study encourages the researcher to use a variety of methods and data types in a single study. 20 21 These can be solely qualitative, solely quantitative or a mixture of both. The latter option allows the researcher to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the case and improve the accuracy of the findings. The four above-mentioned key features of case study are shown in table 1 , using the example of a mixed methods case study evaluation. 22
There are many potential applications for case study research. While often misconstrued as having only an exploratory role, case study research can be used for descriptive and explanatory research (p7–9). 3 Family medicine and community health researchers can use case study research for evaluating a variety of educational programmes, clinical programmes or community programmes.
- Case study illustration from family medicine
In the featured study, Japanese family medicine residents received standardised patient instructor-based training in female breast, pelvic, male genital and prostate examinations as part of an international training collaboration to launch a new family medicine residency programme. 22 From family medicine residents, trainers and staff, the authors collected and analysed data from post-training feedback, semistructured interviews and a web-based questionnaire. While the programme was perceived favourably, they noted barriers to reinforcement in their home training programme, and taboos regarding gender-specific healthcare appear as barriers to implementing a similar programme in the home institution.
- A step-by-step description of the process of carrying out a case study
As shown in table 2 and illustrated using the article by Shultz et al , 22 case study research generally includes 10 steps. While commonly conducted in this order, the steps do not always occur linearly as data collection and analysis may occur over several iterations or implemented with a slightly different order.
Step 1. Conduct a literature review
During the literature review, researchers systematically search for publications, select those most relevant to the study’s purpose, critically appraise them and summarise the major themes. The literature review helps researchers ascertain what is and is not known about the phenomenon under study, delineate the scope and research questions of the study, and develop an academic or practical justification for the study. 23
Step 2. Formulate the research questions
Research questions critically define in operational terms what will be researched and how. They focus the study and play a key role in guiding design decisions. Key decisions include the case selection and choice of a case study design most suitable for the study. According to Fraenkel et al , 24 the key attributes of good research questions are (1) feasibility, (2) clarity, (3) significance, (4) connection to previous research identified in the literature and (5) compliance with ethical research standards.
Step 3. Ensure that a case study is appropriate
Before commencing the study, researchers should ensure that case study design embodies the most appropriate strategy for answering the study questions. The above-noted four key features—in depth examination of phenomena, naturalness, a focus on context and the use of a combination of methods—should be reflected in the research questions as well as subsequent design decisions.
Step 4. Determine the type of case study design
Researchers need to choose a specific case study design. Sometimes, researchers may define the case first (step 5), for example, in a programme evaluation, and the case may need to be defined before determining the type. Yin’s 3 typology is based on two dimensions, whether the study will examine a single case or multiple cases, and whether the study will focus on a single or multiple units of analysis. Figure 1 illustrates these four types of design using a hypothetical example of a programme evaluation. Table 3 shows an example of each type from the literature.
Types of case study designs. 3 21
In type 1 holistic single case design , researchers examine a single programme as the sole unit of analysis. In type 2 embedded single case design , the interest is not exclusively in the programme, but also in its different subunits, including sites, staff and participants. These subunits constitute the range of units of analysis. In type 3 holistic multiple case design , researchers conduct a within and cross-case comparison of two or more programmes, each of which constitutes a single unit of analysis. A major strength of multiple case designs is that they enable researchers to develop an in depth description of each case and to identify patterns of variation and similarity between the cases. Multiple case designs are likely to have stronger internal validity and generate more insightful findings than single case designs. They do this by allowing ‘examination of processes and outcomes across many cases, identification of how individual cases might be affected by different environments, and the specific conditions under which a finding may occur’ (p583). 25 In type 4 embedded multiple case design , a variant of the holistic multiple case design, researchers perform a detailed examination of the subunits of each programme, rather than just examining each case as a whole.
Step 5. Define the boundaries of the case(s) and select the case(s)
Miles et al 26 define a case as ‘a phenomenon of some sort occurring in a bounded context’ (p28). What is and is not the case and how the case fits within its broader context should be explicitly defined. As noted in step 4, this step may occur before choice of the case study type, and the process may actually occur in a back-and-forth fashion. A case can entail an individual, a group, an organisation, an institution or a programme. In this step, researchers delineate the spatial and temporal boundaries of the case, that is, ‘when and where it occurred, and when and what was of interest’ (p390). 9 Aside from ensuring the coherence and consistency of the study, bounding the case ensures that the planned research project is feasible in terms of time and resources. Having access to the case and ensuring ethical research practice are two central considerations in case selection. 1
Step 6. Prepare to collect data
Before beginning the data collection, researchers need a study protocol that describes in detail the methods of data collection. The protocol should emphasise the coherence between the data collection methods and the research questions. According to Yin, 3 a case study protocol should include (1) an overview of the case study, (2) data collection procedures, (3) data collection questions and (4) a guide for the case study report. The protocol should be sufficiently flexible to allow researchers to make changes depending on the context and specific circumstances surrounding each data collection method.
Step 7. Collect and organise the data
While case study is often portrayed as a qualitative approach to research (eg, interviews, focus groups or observations), case study designs frequently rely on multiple data sources, including quantitative data (eg, surveys or statistical databases). A growing number of authors highlight the ways in which the use of mixed methods within case study designs might contribute to developing ‘a more complete understanding of the case’ (p902), 21 shedding light on ‘the complexity of a case’ (p118) 27 or increasing ‘the internal validity of a study’ (p6). 1 Guetterman and Fetters 21 explain how a qualitative case study can also be nested within a mixed methods design (ie, be considered the qualitative component of the design). An interesting strategy for organising multiple data sources is suggested by Yin. 3 He recommends using a case study database in which different data sources (eg, audio files, notes, documents or photographs) are stored for later retrieval or inspection. See guidance from Creswell and Hirose 28 for conducting a survey and qualitative data collection in mixed methods and DeJonckheere 29 on semistructured interviewing.

Step 8. Analyse the data
Bernard and Ryan 30 define data analysis as ‘the search for patterns in data and for ideas that help explain why these patterns are there in the first place’ (p109). Depending on the case study design, analysis of the qualitative and quantitative data can be done concurrently or sequentially. For the qualitative data, the first step of the analysis involves segmenting the data into coding units, ascribing codes to data segments and organising the codes in a coding scheme. 31 Depending on the role of theory in the study, an inductive, data-driven approach can be used where meaning is found in the data, or a deductive, concept-driven approach can be adopted where predefined concepts derived from the literature, or previous research, are used to code the data. 32 The second step involves searching for patterns across codes and subsets of respondents, so major themes are identified to describe, explain or predict the phenomenon under study. Babchuk 33 provides a step-by-step guidance for qualitative analysis in this issue. When conducting a single case study, the within-case analysis yields an in depth, thick description of the case. When the study involves multiple cases, the cross-comparison analysis elicits a description of similarities and divergence between cases and may generate explanations and theoretical predictions regarding other cases. 26
For the quantitative part of the case study, data are entered in statistical software packages for conducting descriptive or inferential analysis. Guetterman 34 provides a step-by-step guidance on basic statistics. In case study designs where both data strands are analysed simultaneously, analytical techniques include pattern matching, explanation building, time-series analysis and creating logic models (p142–167). 3
Step 9. Write the case study report
The case study report should have the following three characteristics. First, the description of the case and its context should be sufficiently comprehensive to allow the reader to understand the complexity of the phenomena under study. 35 Second, the data should be presented in a concise and transparent manner to enable the reader to question, or to re-examine, the findings. 36 Third, the report should be adapted to the interests and needs of its primary audience or audiences (eg, academics, practitioners, policy-makers or funders of research). Yin 3 suggests six formats for organising case study reports, namely linear-analytic, comparative, chronological, theory building, suspense and unsequenced structures. To facilitate case transferability and applicability to other similar contexts, the case study report must include a detailed description of the case.
Step 10. Appraise quality
Although presented as the final step of the case study process, quality appraisal should be considered throughout the study. Multiple criteria and frameworks for appraising the quality of case study research have been suggested in the literature. Yin 3 suggests the following four criteria: construct validity (ie, the extent to which a study accurately measures the concepts that it claims to investigate), internal validity (ie, the strength of the relationship between variables and findings), external validity (ie, the extent to which the findings can be generalised) and reliability (ie, the extent to which the findings can be replicated by other researchers conducting the same study). Yin 37 also suggests using two separate sets of guidelines for conducting case study research and for appraising the quality of case study proposals. Stake 4 presents a 20-item checklist for critiquing case study reports, and Creswell and Poth 38 and Denscombe 39 outline a number of questions to consider. Since these quality frameworks have evolved from different disciplinary and philosophical backgrounds, the researcher’s approach should be coherent with the epistemology of the study. Figure 2 provides a quality appraisal checklist adapted from Creswell and Poth 38 and Denscombe. 39
Checklist for evaluating the quality of a case study. 38 39
The challenges to conducting case study research include rationalising the literature based on literature review, writing the research questions, determining how to bound the case, and choosing among various case study purposes and designs. Factors held in common with other methods include analysing and presenting the findings, particularly with multiple data sources.
Other resources
Resources with more in depth guidance on case study research include Merriam, 17 Stake 4 and Yin. 3 While each reflects a different perspective on case study research, they all provide useful guidance for designing and conducting case studies. Other resources include Creswell and Poth, 38 Swanborn 2 and Tight. 40 For mixed methods case study designs, Creswell and Clark, 27 Guetterman and Fetters, 21 Luck et al , 6 and Plano Clark et al 41 provide guidance. Byrne and Ragin’s 42 The SAGE Handbook of Case-Based Methods and Mills et al ’s 43 Encyclopedia of case study research provide guidance for experienced case study researchers.
- Conclusions
Family medicine and community health researchers engage in a wide variety of clinical, educational, research and administrative programmes. Case study research provides a highly flexible and powerful research tool to evaluate rigorously many of these endeavours and disseminate this information.
Contributors: SF and MDF conceived and drafted the manuscript, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding: The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent for publication: Not required.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the help of Dick Edelstein and Marie-Hélène Paré in editing the final manuscript.
- Little SH , Motohara S , Miyazaki K , et al. Prenatal group visit program for a population with limited English proficiency. J Am Board Fam Med 2013 ; 26 : 728–37 . doi:10.3122/jabfm.2013.06.130005 • Google Scholar
- Peterson JC , Rogers EM , Cunningham-Sabo L , et al. A framework for research utilization applied to seven case studies. Am J Prev Med 2007 ; 33 : S21–S34 . doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2007.03.009 • Google Scholar
- Shea CM , Halladay JR , Reed D , et al. Integrating a health-related-quality-of-life module within electronic health records: a comparative case study assessing value added. BMC Health Serv Res 2012 ; 12 . doi:10.1186/1472-6963-12-67 • Google Scholar
- Received : 30 November 2018
- Accepted : 23 January 2019
- First Published : 23 March 2019
- Publication history
- Rapid Responses
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
Distinguishing case study as a research method from case reports as a publication type
Kristine m alpi , mls, mph, phd, ahip, john jamal evans , phd.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Received 2018 Oct 1; Accepted 2018 Oct 1; Issue date 2019 Jan.
Articles in this journal are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
The purpose of this editorial is to distinguish between case reports and case studies. In health, case reports are familiar ways of sharing events or efforts of intervening with single patients with previously unreported features. As a qualitative methodology, case study research encompasses a great deal more complexity than a typical case report and often incorporates multiple streams of data combined in creative ways. The depth and richness of case study description helps readers understand the case and whether findings might be applicable beyond that setting.
Single-institution descriptive reports of library activities are often labeled by their authors as “case studies.” By contrast, in health care, single patient retrospective descriptions are published as “case reports.” Both case reports and case studies are valuable to readers and provide a publication opportunity for authors. A previous editorial by Akers and Amos about improving case studies addresses issues that are more common to case reports; for example, not having a review of the literature or being anecdotal, not generalizable, and prone to various types of bias such as positive outcome bias [ 1 ]. However, case study research as a qualitative methodology is pursued for different purposes than generalizability. The authors’ purpose in this editorial is to clearly distinguish between case reports and case studies. We believe that this will assist authors in describing and designating the methodological approach of their publications and help readers appreciate the rigor of well-executed case study research.
Case reports often provide a first exploration of a phenomenon or an opportunity for a first publication by a trainee in the health professions. In health care, case reports are familiar ways of sharing events or efforts of intervening with single patients with previously unreported features. Another type of study categorized as a case report is an “N of 1” study or single-subject clinical trial, which considers an individual patient as the sole unit of observation in a study investigating the efficacy or side effect profiles of different interventions. Entire journals have evolved to publish case reports, which often rely on template structures with limited contextualization or discussion of previous cases. Examples that are indexed in MEDLINE include the American Journal of Case Reports , BMJ Case Reports, Journal of Medical Case Reports, and Journal of Radiology Case Reports . Similar publications appear in veterinary medicine and are indexed in CAB Abstracts, such as Case Reports in Veterinary Medicine and Veterinary Record Case Reports .
As a qualitative methodology, however, case study research encompasses a great deal more complexity than a typical case report and often incorporates multiple streams of data combined in creative ways. Distinctions include the investigator’s definitions and delimitations of the case being studied, the clarity of the role of the investigator, the rigor of gathering and combining evidence about the case, and the contextualization of the findings. Delimitation is a term from qualitative research about setting boundaries to scope the research in a useful way rather than describing the narrow scope as a limitation, as often appears in a discussion section. The depth and richness of description helps readers understand the situation and whether findings from the case are applicable to their settings.
CASE STUDY AS A RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Case study as a qualitative methodology is an exploration of a time- and space-bound phenomenon. As qualitative research, case studies require much more from their authors who are acting as instruments within the inquiry process. In the case study methodology, a variety of methodological approaches may be employed to explain the complexity of the problem being studied [ 2 , 3 ].
Leading authors diverge in their definitions of case study, but a qualitative research text introduces case study as follows:
Case study research is defined as a qualitative approach in which the investigator explores a real-life, contemporary bounded system (a case) or multiple bound systems (cases) over time, through detailed, in-depth data collection involving multiple sources of information, and reports a case description and case themes. The unit of analysis in the case study might be multiple cases (a multisite study) or a single case (a within-site case study). [ 4 ]
Methodologists writing core texts on case study research include Yin [ 5 ], Stake [ 6 ], and Merriam [ 7 ]. The approaches of these three methodologists have been compared by Yazan, who focused on six areas of methodology: epistemology (beliefs about ways of knowing), definition of cases, design of case studies, and gathering, analysis, and validation of data [ 8 ]. For Yin, case study is a method of empirical inquiry appropriate to determining the “how and why” of phenomena and contributes to understanding phenomena in a holistic and real-life context [ 5 ]. Stake defines a case study as a “well-bounded, specific, complex, and functioning thing” [ 6 ], while Merriam views “the case as a thing, a single entity, a unit around which there are boundaries” [ 7 ].
Case studies are ways to explain, describe, or explore phenomena. Comments from a quantitative perspective about case studies lacking rigor and generalizability fail to consider the purpose of the case study and how what is learned from a case study is put into practice. Rigor in case studies comes from the research design and its components, which Yin outlines as (a) the study’s questions, (b) the study’s propositions, (c) the unit of analysis, (d) the logic linking the data to propositions, and (e) the criteria for interpreting the findings [ 5 ]. Case studies should also provide multiple sources of data, a case study database, and a clear chain of evidence among the questions asked, the data collected, and the conclusions drawn [ 5 ].
Sources of evidence for case studies include interviews, documentation, archival records, direct observations, participant-observation, and physical artifacts. One of the most important sources for data in qualitative case study research is the interview [ 2 , 3 ]. In addition to interviews, documents and archival records can be gathered to corroborate and enhance the findings of the study. To understand the phenomenon or the conditions that created it, direct observations can serve as another source of evidence and can be conducted throughout the study. These can include the use of formal and informal protocols as a participant inside the case or an external or passive observer outside of the case [ 5 ]. Lastly, physical artifacts can be observed and collected as a form of evidence. With these multiple potential sources of evidence, the study methodology includes gathering data, sense-making, and triangulating multiple streams of data. Figure 1 shows an example in which data used for the case started with a pilot study to provide additional context to guide more in-depth data collection and analysis with participants.
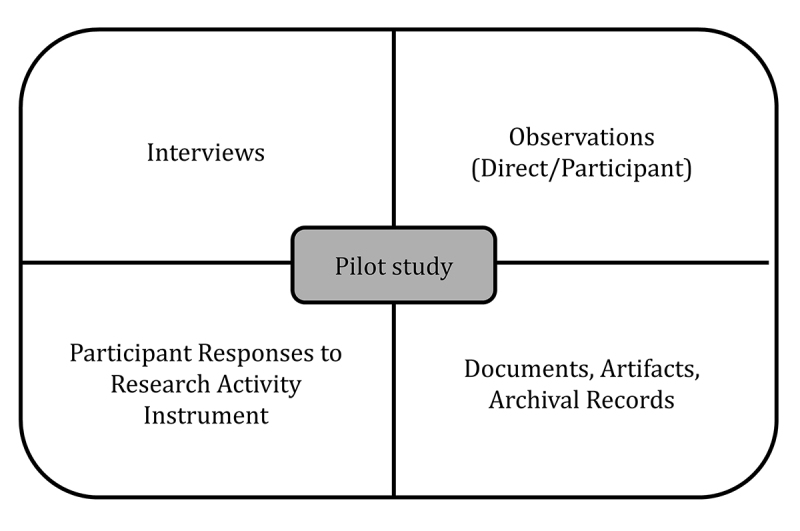
Key sources of data for a sample case study
VARIATIONS ON CASE STUDY METHODOLOGY
Case study methodology is evolving and regularly reinterpreted. Comparative or multiple case studies are used as a tool for synthesizing information across time and space to research the impact of policy and practice in various fields of social research [ 9 ]. Because case study research is in-depth and intensive, there have been efforts to simplify the method or select useful components of cases for focused analysis. Micro-case study is a term that is occasionally used to describe research on micro-level cases [ 10 ]. These are cases that occur in a brief time frame, occur in a confined setting, and are simple and straightforward in nature. A micro-level case describes a clear problem of interest. Reporting is very brief and about specific points. The lack of complexity in the case description makes obvious the “lesson” that is inherent in the case; although no definitive “solution” is necessarily forthcoming, making the case useful for discussion. A micro-case write-up can be distinguished from a case report by its focus on briefly reporting specific features of a case or cases to analyze or learn from those features.
DATABASE INDEXING OF CASE REPORTS AND CASE STUDIES
Disciplines such as education, psychology, sociology, political science, and social work regularly publish rich case studies that are relevant to particular areas of health librarianship. Case reports and case studies have been defined as publication types or subject terms by several databases that are relevant to librarian authors: MEDLINE, PsycINFO, CINAHL, and ERIC. Library, Information Science & Technology Abstracts (LISTA) does not have a subject term or publication type related to cases, despite many being included in the database. Whereas “Case Reports” are the main term used by MEDLINE’s Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) and PsycINFO’s thesaurus, CINAHL and ERIC use “Case Studies.”
Case reports in MEDLINE and PsycINFO focus on clinical case documentation. In MeSH, “Case Reports” as a publication type is specific to “clinical presentations that may be followed by evaluative studies that eventually lead to a diagnosis” [ 11 ]. “Case Histories,” “Case Studies,” and “Case Study” are all entry terms mapping to “Case Reports”; however, guidance to indexers suggests that “Case Reports” should not be applied to institutional case reports and refers to the heading “Organizational Case Studies,” which is defined as “descriptions and evaluations of specific health care organizations” [ 12 ].
PsycINFO’s subject term “Case Report” is “used in records discussing issues involved in the process of conducting exploratory studies of single or multiple clinical cases.” The Methodology index offers clinical and non-clinical entries. “Clinical Case Study” is defined as “case reports that include disorder, diagnosis, and clinical treatment for individuals with mental or medical illnesses,” whereas “Non-clinical Case Study” is a “document consisting of non-clinical or organizational case examples of the concepts being researched or studied. The setting is always non-clinical and does not include treatment-related environments” [ 13 ].
Both CINAHL and ERIC acknowledge the depth of analysis in case study methodology. The CINAHL scope note for the thesaurus term “Case Studies” distinguishes between the document and the methodology, though both use the same term: “a review of a particular condition, disease, or administrative problem. Also, a research method that involves an in-depth analysis of an individual, group, institution, or other social unit. For material that contains a case study, search for document type: case study.” The ERIC scope note for the thesaurus term “Case Studies” is simple: “detailed analyses, usually focusing on a particular problem of an individual, group, or organization” [ 14 ].
PUBLICATION OF CASE STUDY RESEARCH IN LIBRARIANSHIP
We call your attention to a few examples published as case studies in health sciences librarianship to consider how their characteristics fit with the preceding definitions of case reports or case study research. All present some characteristics of case study research, but their treatment of the research questions, richness of description, and analytic strategies vary in depth and, therefore, diverge at some level from the qualitative case study research approach. This divergence, particularly in richness of description and analysis, may have been constrained by the publication requirements.
As one example, a case study by Janke and Rush documented a time- and context-bound collaboration involving a librarian and a nursing faculty member [ 15 ]. Three objectives were stated: (1) describing their experience of working together on an interprofessional research team, (2) evaluating the value of the librarian role from librarian and faculty member perspectives, and (3) relating findings to existing literature. Elements that signal the qualitative nature of this case study are that the authors were the research participants and their use of the term “evaluation” is reflection on their experience. This reads like a case study that could have been enriched by including other types of data gathered from others engaging with this team to broaden the understanding of the collaboration.
As another example, the description of the academic context is one of the most salient components of the case study written by Clairoux et al., which had the objectives of (1) describing the library instruction offered and learning assessments used at a single health sciences library and (2) discussing the positive outcomes of instruction in that setting [ 16 ]. The authors focus on sharing what the institution has done more than explaining why this institution is an exemplar to explore a focused question or understand the phenomenon of library instruction. However, like a case study, the analysis brings together several streams of data including course attendance, online material page views, and some discussion of results from surveys. This paper reads somewhat in between an institutional case report and a case study.
The final example is a single author reporting on a personal experience of creating and executing the role of research informationist for a National Institutes of Health (NIH)–funded research team [ 17 ]. There is a thoughtful review of the informationist literature and detailed descriptions of the institutional context and the process of gaining access to and participating in the new role. However, the motivating question in the abstract does not seem to be fully addressed through analysis from either the reflective perspective of the author as the research participant or consideration of other streams of data from those involved in the informationist experience. The publication reads more like a case report about this informationist’s experience than a case study that explores the research informationist experience through the selection of this case.
All of these publications are well written and useful for their intended audiences, but in general, they are much shorter and much less rich in depth than case studies published in social sciences research. It may be that the authors have been constrained by word counts or page limits. For example, the submission category for Case Studies in the Journal of the Medical Library Association (JMLA) limited them to 3,000 words and defined them as “articles describing the process of developing, implementing, and evaluating a new service, program, or initiative, typically in a single institution or through a single collaborative effort” [ 18 ]. This definition’s focus on novelty and description sounds much more like the definition of case report than the in-depth, detailed investigation of a time- and space-bound problem that is often examined through case study research.
Problem-focused or question-driven case study research would benefit from the space provided for Original Investigations that employ any type of quantitative or qualitative method of analysis. One of the best examples in the JMLA of an in-depth multiple case study that was authored by a librarian who published the findings from her doctoral dissertation represented all the elements of a case study. In eight pages, she provided a theoretical basis for the research question, a pilot study, and a multiple case design, including integrated data from interviews and focus groups [ 19 ].
We have distinguished between case reports and case studies primarily to assist librarians who are new to research and critical appraisal of case study methodology to recognize the features that authors use to describe and designate the methodological approaches of their publications. For researchers who are new to case research methodology and are interested in learning more, Hancock and Algozzine provide a guide [ 20 ].
We hope that JMLA readers appreciate the rigor of well-executed case study research. We believe that distinguishing between descriptive case reports and analytic case studies in the journal’s submission categories will allow the depth of case study methodology to increase. We also hope that authors feel encouraged to pursue submitting relevant case studies or case reports for future publication.
Editor’s note: In response to this invited editorial, the Journal of the Medical Library Association will consider manuscripts employing rigorous qualitative case study methodology to be Original Investigations (fewer than 5,000 words), whereas manuscripts describing the process of developing, implementing, and assessing a new service, program, or initiative—typically in a single institution or through a single collaborative effort—will be considered to be Case Reports (formerly known as Case Studies; fewer than 3,000 words).
- 1. Akers KG, Amos K. Publishing case studies in health sciences librarianship [editorial] J Med Libr Assoc. 2017 Apr;105(2):115–8. doi: 10.5195/jmla.2017.212. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 2. Creswell JW. Qualitative inquiry & research design: choosing among five approaches. 4th ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE; 2018. [ Google Scholar ]
- 3. Yin RK. Case study research: design and methods. 4th ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- 4. Creswell JW. Research design: qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods approaches. 4th ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE; 2014. [ Google Scholar ]
- 5. Yin RK. Case study research and applications: design and methods. 6th ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE; 2018. [ Google Scholar ]
- 6. Stake RE. The art of case study research. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- 7. Merriam SB. Qualitative research and case study applications in education. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- 8. Yazan B. Three approaches to case study methods in education: Yin, Merriam, and Stake. Qual Rep. 2015;20(2):134–52. [ Google Scholar ]
- 9. Bartlett L, Vavrus F. Rethinking case study research: a comparative approach. New York, NY: Routledge; 2017. [ Google Scholar ]
- 10. Walsh RW. Exploring the case study method as a tool for teaching public administration in a cross-national context: pedagogy in theory and practice. European Group of Public Administration Conference, International Institute of Administrative Sciences; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- 11. National Library of Medicine. Case reports: MeSH descriptor data 2018 [Internet] The Library; [cited 1 Sep 2018]. < https://meshb.nlm.nih.gov/record/ui?ui=D002363 >. [ Google Scholar ]
- 12. National Library of Medicine. Organizational case studies: MeSH descriptor data 2018 [Internet] The Library; [cited 26 Oct 2018]. < https://meshb.nlm.nih.gov/record/ui?ui=D019982 >. [ Google Scholar ]
- 13. American Psychological Association. APA databases methodology field values [Internet] The Association; 2016. [cited 1 Sep 2018]. < http://www.apa.org/pubs/databases/training/method-values.aspx >. [ Google Scholar ]
- 14. ERIC. Case studies [Internet] ERIC; [cited 1 Sep 2018]. < https://eric.ed.gov/?ti=Case+Studies >. [ Google Scholar ]
- 15. Janke R, Rush K. The academic librarian as co-investigator on an interprofessional primary research team: a case study. Health Inf Libr J. 2014;31(2):116–22. doi: 10.1111/hir.12063. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 16. Clairoux N, Desbiens S, Clar M, Dupont P, St Jean M. Integrating information literacy in health sciences curricula: a case study from Québec. Health Inf Libr J. 2013;30(3):201–11. doi: 10.1111/hir.12025. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 17. Federer L. The librarian as research informationist: a case study. J Med Libr Assoc. 2013 Oct;101(4):298–302. doi: 10.3163/1536-5050.101.4.011. doi: 10.3163/1536-5050.101.4.011. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 18. Medical Library Association. Journal of the Medical Library Association author guidelines: submission categories and format guidelines [Internet] The Association; [cited 1 Sep 2018]. < http://jmla.mlanet.org/ojs/jmla/about/submissions >. [ Google Scholar ]
- 19. Martin ER. Team effectiveness in academic medical libraries: a multiple case study. J Med Libr Assoc. 2006 Jul;94(3):271–8. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 20. Hancock DR, Algozzine B. Doing case study research: a practical guide for beginning researchers. New York, NY: Teachers College Press; 2017. [ Google Scholar ]
- View on publisher site
- PDF (185.2 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research.1 However, very simply… 'a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units'.1 A case study has also been described as an intensive, systematic investigation of a ...
Case study research is defined as a qualitative approach in which the investigator explores a real-life, contemporary bounded system (a case) or multiple bound systems (cases) over time, through detailed, in-depth data collection involving multiple sources of information, and reports a case description and case themes.
case study EBM (1) An in-depth analysis and systematic description of one patient or group of similar patients to promote a detailed understanding of their circumstances.
The storm caused more than 10,000 deaths; according to Conserving the Peace: Resources, Livelihoods and Security, a 2003 collection of case studies published by the International Institute for Sustainable Development, the subsequent flooding and landslides wiped out more than 2,000 potable water systems in Honduras and Nicaragua alone, left millions without dependable drinking water, and ...
A case report study is a type of clinical research that involves the detailed description of a single patient or a small number of patients with a specific disease, condition, or treatment. It is a written account of a patient's medical history, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and outcome, with the aim of providing a comprehensive ...
The case study approach allows in-depth, multi-faceted explorations of complex issues in their real-life settings. ... Definition; Stake "A case study is both the process of learning about the case and the product of our learning" (p.237) Yin[1,27,28] ... Doolin B. Power and resistance in the implementation of a medical management information ...
There are many potential applications for case study research. While often misconstrued as having only an exploratory role, case study research can be used for descriptive and explanatory research (p7-9). 3 Family medicine and community health researchers can use case study research for evaluating a variety of educational programmes, clinical programmes or community programmes.
The aim of this article is to introduce family medicine researchers to case study research, a rigorous research methodology commonly used in the social and health sciences and only distantly related to clinical case reports. The article begins with an overview of case study in the social and health sciences, including its definition, potential applications, historical background and core ...
The value of case studies in the medical literature is controversial among physicians. Despite their limitations, clinical case reports and case series are beneficial tools in graduate medical education. The preparation and presentation of case studies can help students and residents acquire and apply clinical competencies in the areas of ...
For example, the submission category for Case Studies in the Journal of the Medical Library Association (JMLA) limited them to 3,000 words and defined them as "articles describing the process of developing, implementing, ... This definition's focus on novelty and description sounds much more like the definition of case report than the in ...