
- SAP Simple Finance Tutorial
- SAP Simple Finance - Home
- SAP HANA - Introduction
- SAP Simple Finance - Introduction
- SAP Simple Finance - Architecture
- Extend G/L Coding Block
- Universal Journal
- Document Number
- Display Financial Tables
- Deployment Options
- Post & Reverse Documents
- Reporting Options
- SAP Simple Finance - Migration
- Manual Reposting of Costs
- SAP Simple Finance - G/L Accounting
- Create a Primary Cost
- Create a Secondary Cost
- SAP Simple Finance - Ledger Mgmt
- Asset Accounting
- Create an Asset
- SAP Simple Finance - Asset Scrapping

Create Default Account Assignment
- Management Accounting
- Profitability Analysis
- Period Lock Transaction
- New Period Closing Program
- SAP Simple Finance - Integration
- SAP Simple Finance - IBPF
- Consultant Capabilities
- SAP Simple Finance Resources
- SAP Simple Finance - Quick Guide
- SAP Simple Finance - Resources
- SAP Simple Finance - Discussion
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
You can create a default account assignment for any cost element using Transaction code OKB9. Later, you can also post a document to check if that account assignment works.
Transaction code - OKB9

Step 1 − To create a new Account Assignment, click New Entries

Step 2 − In the next window, you have to enter the following fields −
- The values of CoCd box
- The value in Cost Elem. box
- The value in the Cost Ctr box

Step 3 − To save the entry, click the Save button at the top
Step 4 − To post a test document to check that the account assignment works, use Transaction code fb50 . In the next window, click Tree On.

Step 5 − Select the Screen Variant in the next window and click Tree Off button.

Step 6 − In the next window, enter the following details −
- The value in Doc Header Box
- Select entry Debit by clicking it
- Amount in doc. Curr. Box
- Select entry H credit by clicking it
- Amount in doc.curr. box

Step 7 − To make the document assignment, click the Save button at the top.
Explaining Account Assignment Derivation
After completing this lesson, you will be able to:
- Explain account assignment derivation and high-level concepts
- Describe the derivation of a budget account
- Describe the derivation of funds, grants, and functional areas
- Describe the derivation of budget periods
- Describe the derivation of cost centers
- Explain the substitution tool
- Describe specific derivation scenarios for integration components
Introduction and High-Level Concept
The activation of Public Sector Management in SAP S/4HANA Cloud requires business transactions with unique PSM account assignments to be posted. A selection of posting factors is predefined by SAP according to the business transaction involved. Other factors must be defined by the customer as automatic account assignment derivations, prefilled with default values, or entered manually.
The following figure, Overview of Derivation Options , provides an overview of the factors that influence the posting of PSM business transactions in financial accounting.

Derivation Events - When will Derivations be Used ?
The derivations described in this lesson are for the following:
Commitment Documents
Financial documents.
For financial documents, this lesson focuses on budgetary relevant lines (for example, expenditure and revenues). Non-budgetary lines, such as liabilities or bank lines, are covered in the chapter document splitting.
Master/Transactional Data
Other master/transactional data such as assets, CLM contracts, HR personal, treasury instruments, time sheet tasks, and so on.
For these objects, the account assignments are derived (or entered) and stored. In later steps, these objects generate commitments or FI documents. The account assignment stored in these objects will then be used into the asset master. Later on all asset transactions (for example, acquisitions, deprecations, and alike) are populated with the fund from the asset master.
Derivation Dependency on G/L Attributes
Line items in commitment and financial documents are treated differently when it comes to derivations, depending on the type of the line item. The type of the line item has been derived from the G/L account in this line item. Therefore, it is important that a line item is first populated with a G/L account before any derivation can take place.
The main indicator in the G/L Account master is the budget consumption type.
The following overarching rules apply to G/L accounts:
Dependency on GL Account Attributes
G/L account: PSM attributes for budgeting:

- The GL account attributes are maintained in the G/L account master data under the Public Sector Management Data tab.
- The budget consumption type of the G/L account is pre-delivered and cannot be changed.
Derivation Target Fields - What Will Be Derived?
Fields to be derived in the public sector management: what will be derived.
- Described only under cash flow reporting
- Described only under grants management
Entering versus Deriving Account Assignments
Account assignment can be either:
Derived automatically without the ability for the user to change the values. The user will not see the resulting account assignment on the input screen, but only see the result using reporting.
Example: The budget account is always derived automatically and only available through reporting.
Derived automatically without the ability for the user to change the values. The user sees the resulting account assignment on the input screen.
Example: A fixed fund assignment is set up in the cost center. When this cost center is being used in an expense line, the user cannot overwrite this fixed assignment.
Derived automatically as proposal. The user is able to change the proposed account assignment.
Example: A (non-fixed) fund assignment is set-up in the cost center. When this cost center is being used in an expense line, the user sees the fund assignment, but can change/overwrite it to a different fund.
Entered manually without any derivation. The user has to enter the account assignment as no derivation rule applies.
Example: No fund assignment is set up in the cost center. When this cost center is being used, the user must enter the fund manually (otherwise an error message appears).
Where will the Account Assignments be Derived from?
The following is a list of sources where account assignment can be stored in order to be transferred for population of commitment and actual documents.
Sources of PSM Account Assignments
The derivation rules are:
- Either system-delivered (hard-coded) and cannot be influenced by the user (for example, derivation for budget accounts)
- Or can be influenced by the user, for example, by adding a fund as a fixed or non-fixed assignment to the cost center
- Or can be set up through configuration (for example, using the substitution rule)
Paradigm for the SAP S/4HANA Cloud version: most derivations work with the standard system-delivered rule without configuration. Configurations can be used to deviate from the standard behavior.
In exceptional cases, the rules can contradict. Configured rules cannot overwrite system-delivered fixed assignments.
Example: If Cost Center1 is assigned to Fund1 as a fixed assignment, but the substitution rule has been set up as a rule to derive Fund2 from Cost Center1 , then the system keeps Fund1 , but will raise a message. This message can be configured as a warning or error.

Derivation of Budget Account
General delivered rule:.
The budget account is taken 1:1 from the G/L account for all line items with budget consumption types 95,99. The budget account is always derived and cannot be entered.
Example: For a cost posting to account 61002000, the budget account is determined as 61002000. This cannot be influenced.
Exceptions:
For assets, there is a specific configuration called Budget Account Derivation for Assets . It is possible to overwrite a different budget account.
Example: An asset acquisition or purchase order posting to a balance sheet account for office equipment 16105000 will use the account 80005000 (expense for office equipment) instead.
For down payments, the budget account is used either from referenced commitment documents or from a specific configuration called Budget Account Derivation for Down Payments without PO reference .
Example: A down payment with reference to a purchase order using G/L account 51100000 (cost for raw material) will post to budget account 5110000 instead of the down payment liability account.
Derivation of Fund, Grant, Functional Area
The following paragraph describes the derivation of these three account assignments:
- The derivation rule for these three account assignments is identical and mainly done through sources.
- Cost center and WBS element
- External data such as HR master, assets, CLM contracts, and so on
- Predecessor documents such as earmarked funds and purchase order/requisition
- Substitution tool
- For asset lines, these account assignment are always taken from the asset master (no exception).
- For other expenditure lines and master data with cost center and WBS elements as sources, certain priorities apply (this will be explained further later on).

Cost Center-Based Derivation
Using the Manage Cost Centers app, you can define default values for the PSM account assignment elements in a cost center master record. If you also set the Fixed Assignment indicator for a PSM field, the default value can no longer be changed manually when postings are made to that cost center. If the indicator is not set, the system proposes the default values, but these can be overwritten when postings are made.

The previous figure shows an example of how the PSM field values (fund, functional area, and grant) can be proposed from a cost center master record or entered manually when a posting is made:
- The functional area value is derived from the cost center master data and cannot be changed manually during posting because the fixed indicator is set in the cost center master record.
- The fund value is also derived from the cost center master data. Since the fixed indicator is not set, it is a default value for the fund that can be changed manually for postings.
- No grant value is defined in the cost center master record, that is no value is derived from the cost center master data. The grant value must be entered manually during postings.
Assignment of PSM Account Assignments and Fixed Flags for Cost Centers and WBS Elements
The following figures show the assignment of PSM account assignments and the fixed flags for cost centers and WBS elements.

If a situation occurs where a cost center and WBS element are present in the same posting line item, and both supply a PSM account assignment, then the following priority (depicted previously) is followed.
- These rules apply for commitments, actuals, and master data derivations.
- Real/statistical indicators are described in controlling.
- (*) PSM account assignment might be in line already from manual input, predecessor document, or API call.
Example: A document is posted against a statistical WBS element (assigned to functional area FA1) and a real cost center (assigned to functional area FA2).
No functional area is manually input.
The system derives functional area FA2.
Derivation of Budget Period
- As the budget period needs to have the same frequency as the fund, the fund needs to be derived before the budget period.
When the fund is available, the system uses the budget consumption date and the frequency to derive exactly one budget period (as it is not possible to have several budget periods for the same date/same frequency).
Example: Fund1 has a yearly frequency. The budget consumption date is the 01/01/2020. The system derives the budget period "2020" automatically.
If the fund is changed and as a result the frequency changes (for example from yearly to overall), the system tries to automatically change the budget period as well.
Example: The user has used an internal fund for a grant posting with yearly frequency, and the system derived the budget period 2020. Now, the user changed the fund to an external fund with overall frequency. Then the system automatically adjusts the budget period to OVERALL . These changes only occur in documents that are not yet posted.
Budget periods can differ from the budget consumption date through inheritance through the document chain (upward/downward adjustment rules might apply) or (if allowed) through manual adjustment.
Example: A goods receipt in fiscal year 2021 inherits the budget period 2020 from a prior year purchase order.
- Refer as well to the specific chapter Describing Year-End Processing .

Derivation of Cost Center
For every budget-relevant posting where the budget consumption type of the G/L account is set to 99, 95, or 61 (expenses/revenues/down payments), the cost center is a required field once PSM has been activated. As a result, the cost center must be populated in all these lines. The lines can be distinguished into the following:
These lines are populated through manual input (or non-PSM derivations/substitutions).
Down payments
These lines are populated through the cost center from commitments or using manual input (for example, in down payment requests).
Revenue lines
These lines must be populated through manual input (for example, for a FI-AR invoice) or using substitution rules (for example, for an SD bill).
Balance sheet account lines
These lines must be populated through PSM derivations. The main sources are as follows:
- For asset balance sheet line items, the cost center from the asset master
- For warehouse balance sheet line items, the cost center from PSM configuration (see specific derivations)
Derivation of Cost Center from WBS Elements
For cost or revenue lines where only a WBS element is entered in the posting, the standard delivered (hard-coded) PSM derivation derives automatically the cost center from the WBS element.
Substitution Tool
Customers can create their own rules with the substitution tool (available for user BPC_EXPERT). The business context for PSM account assignment derivation is "Public Sector" and the event is "Coding Block for Public Sector Management".
Rules must be active to be executed:
- A rule consists of a precondition and a substitution section.- All preconditions need to be fulfilled in order to process the substitution section.- For the precondition, many fields can be used as parameters. Through associations, it is possible to use further attributes of these fields (for example, choose the asset master and any field of the asset master for preconditions). It is also possible to use functions such as substrings and concatenations.- For substitutions it is possible to overwrite existing values, for example, entered manually by the user or derived in an earlier step.
- It is not possible to overwrite fixed assignments from standard delivered rules using the substitution tool (for example, from fixed assignments in the cost center, or the asset master cannot be overwritten by the substitution tool).
- It is possible to trace results during postings. The trace shows SAP standard rules and substitution rules side-by-side through the Substitution/Validation Logs app.

Specific Derivation Scenarios for Integration Components
Other specific derivations.
The following specific derivations exist (more details appear in specific sections).
For some controlling transactions (for example, universal allocations or settlements), the system reads account assignments from existing postings and populates them into sender lines. Specific rules apply for the populations of these lines (for more details, see the chapter on controlling integration).
For asset management all actual and commitment postings are always populated with the fund, grant, functional area, and cost center from the asset master. Budget accounts can exceptionally be derived using the following configuration:

For down payments, it is possible to derive a specific budget account (and cash origin account) for down payments without commitment reference.

For warehouse balance sheet accounts and actual and commitment postings, the PSM account assignments are populated through the following configuration:

For FI-CAC (Contract Accounting Cloud), all derivations are done through a specific substitution context during the transfer of FI-CA postings into FI-GL. PSM account assignments are not derived and stored in FI-CA.

For SD billing, the substitution tool (with business context "Coding Block") is mandatory to derive a cost center. The cost center can then be used to derive further required account assignments (for example, the fund). The condition ReferenceDocumentType (Field) Equal (Operator) to VBRK (Value) is used in the order to process this rule only for billing.
Log in to track your progress & complete quizzes
- What is SAP FICO?
- SAP FICO Training Tutorials for Beginners
- SAP FICO Define Account Group
- SAP FICO Reverse Clearing Document
- Foreign Currency Valuation Configuration
- SAP FICO User Exit for Vendor Master
- FICO Vendor Account Group Table
- SAP FICO Withholding Tax
- SAP FICO Dunning Area
- SAP FICO Cash Management Group
- Assessment Cycle vs Profit Center
- SAP FICO Asset Accounting
- SAP FICO Posting Key for Bank
- SAP FICO Document Type
- SAP FICO Document Number Ranges
- SAP FICO Parked Workflow Configuration
- SAP FICO Classic GL vs New GL
- SAP FICO GL Account for Cash Journal
- SAP FICO Accounts Receivable Process Cycle
- SAP FICO Accounts Receivable Configuration
- GR/IR Accounting Entries and Journal Entries
- SAP FICO Chart of Accounts
- SAP FICO Transaction Codes
- SAP AS11 Create Asset Sub-Number
- SAP Business Area and Profit Center
- SAP Inconsistent Withholding Tax Info
- SAP Active vs Passive Document Splitting
- Reverse MIRO Document in SAP
- SAP FICO Scope and Opportunity
- FICO Certification Cost in India
- SAP FICO Interview Questions
- SAP FICO Tree Menu
What is Account assignment in SAP FICO ?
Updated Apr 01, 2023
Account assignment is a critical aspect of financial accounting and management in any organization. It refers to the process of allocating financial transactions to specific cost or profit centers, projects, or business processes. By properly assigning financial transactions to the appropriate account, organizations can accurately track their expenses, revenues, and profitability. This information can then be used to make informed decisions about resource allocation, cost control, and overall financial management.
In SAP FICO, account assignment is a core module that offers various types of account assignment options, including cost center accounting, profit-center accounting, internal order accounting, and WBS element accounting. These options provide organizations with greater visibility into their financial performance, enabling them to optimize their operations and drive greater value for their stakeholders.
Types of Account Assignment
There are several types of account assignments in SAP FICO, including:
- Cost center accounting
- Profit center accounting
- Internal order accounting
- WBS element accounting
i) Cost center accounting
Cost center accounting is the process of tracking and analyzing costs associated with each department, function, or unit of an organization. SAP FICO provides a module that allows organizations to create and manage cost centers, allocate expenses, and generate reports to track performance.
By tracking expenses at a granular level, organizations can make informed decisions about resource allocation, identify areas of inefficiency, and make changes to improve overall performance, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
ii) Profit center accounting
Profit center accounting is a process that allows organizations to track revenues and expenses at a granular level, providing insights into the profitability of individual business units, product lines, or geographic regions. By allocating revenues and expenses to specific profit centers, organizations can generate reports that help identify areas of high profitability or inefficiency.
SAP FICO provides a comprehensive profit center accounting module that enables organizations to create and manage profit centers, allocate revenues and expenses, and generate reports to analyze profitability. This information can be used to make informed decisions about product lines, investments, and resource allocation, enabling organizations to optimize their profitability and drive growth.
iii) Internal order accounting
Internal order accounting is a process that allows organizations to track and control expenses associated with a specific project, event, or business process. By assigning costs to a specific internal order, organizations can monitor actual expenses versus budgeted expenses, and ensure that resources are allocated efficiently.
iv) WBS element accounting
WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) element accounting is a process that allows organizations to track and control expenses associated with a specific project or work breakdown structure. It involves breaking down large projects into smaller, manageable tasks or work packages, each of which is assigned a WBS element.
Expenses are then allocated to each WBS element to track actual versus planned expenses and ensure that resources are allocated efficiently.
Advantages of Account Assignment
The advantages of account assignment in SAP FICO include:
Better visibility: Account assignment allows organizations to track expenses and revenues at a granular level, providing better visibility into financial performance.
Resource allocation: By tracking expenses and revenues, organizations can make informed decisions about resource allocation, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
Cost control: By identifying areas of inefficiency or waste, organizations can make changes to control costs and improve profitability.
Accurate reporting: Account assignment provides accurate reporting and analytics, enabling organizations to make informed decisions about their financial performance.
Compliance: Account assignment helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements and accounting standards.
How to Define Account Assignment?
Please follow the steps below to define the account assignment:
Execute t-code OKB9 in the SAP command field as shown in the image below.
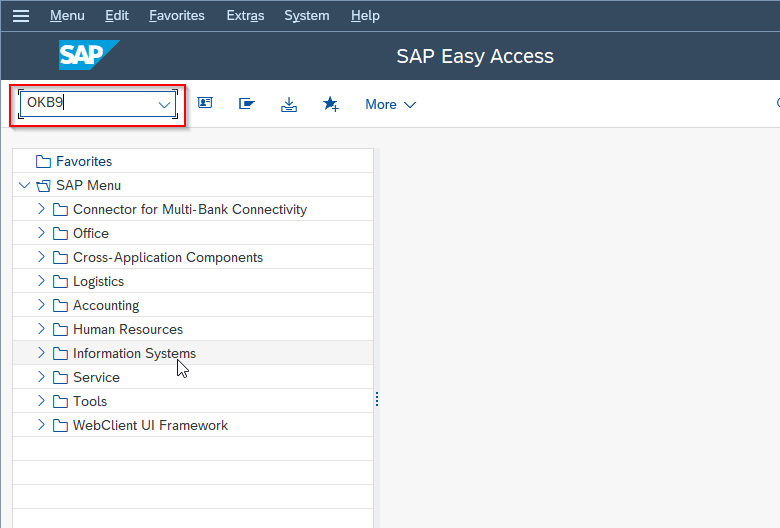
On Change View "Default account assignment": Overview you will see the list of default account assignments.
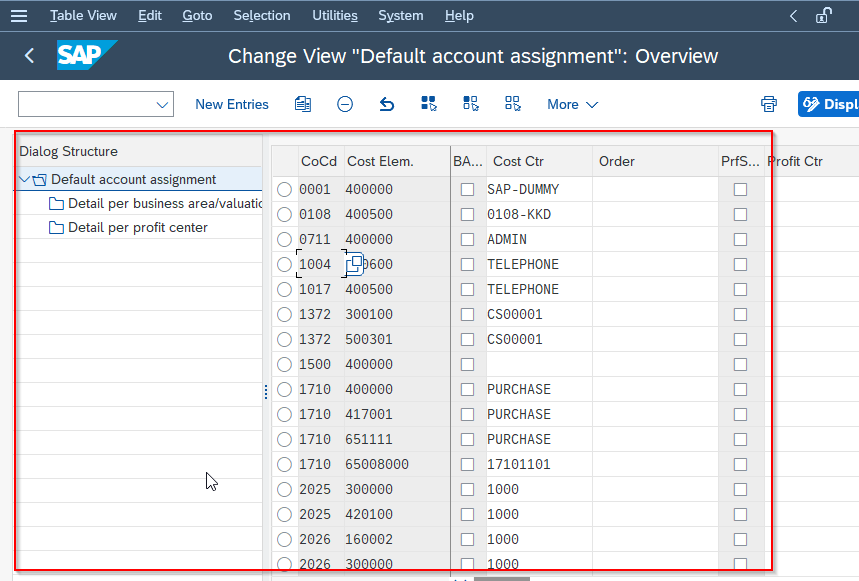
Next, click the New Entries button to create a new account assignment.
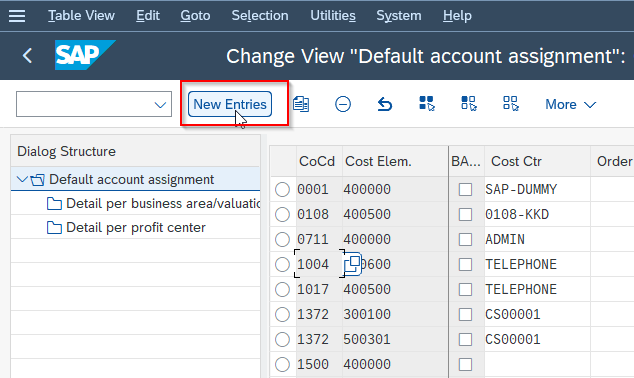
In the next window, enter the following fields:
- Cost Ctr
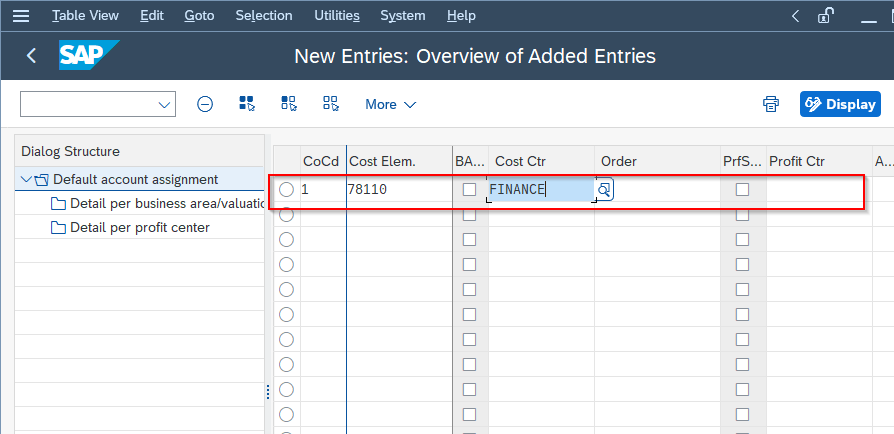
Now click on the Save button to save the new account assignment.
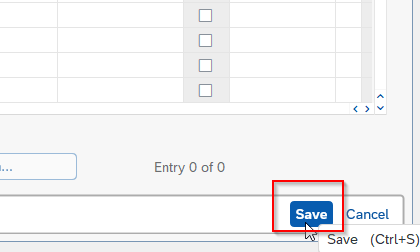
Now in order to post a test document to check that the account assignment works, execute t-code FB50 in the SAP command field.
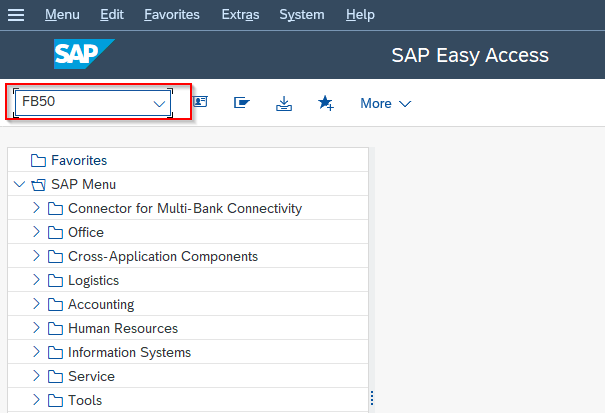
On the next popup enter Company Code as shown below.
.png)
Now on the next window, click Tree On button.
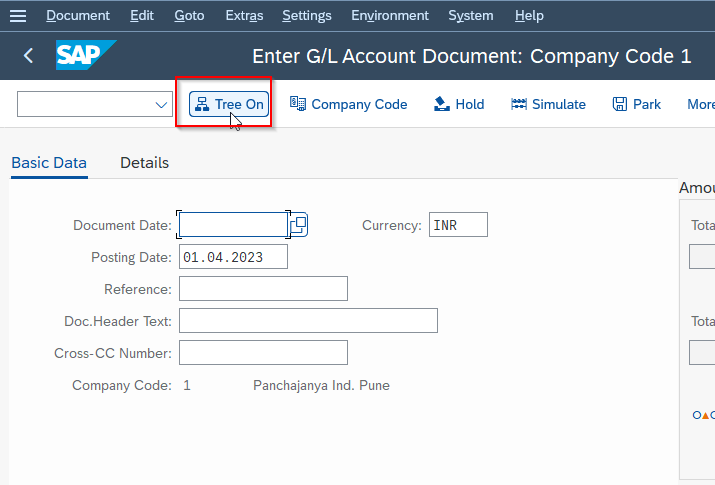
Next, select the Screen Variant in the next window and click Tree Off button.
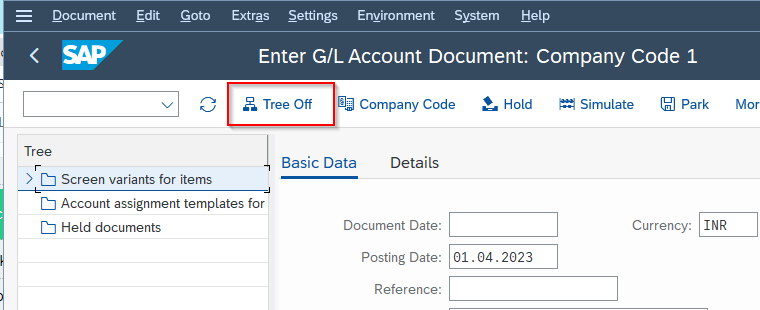
In the next window, enter the following fields according to your requirements:
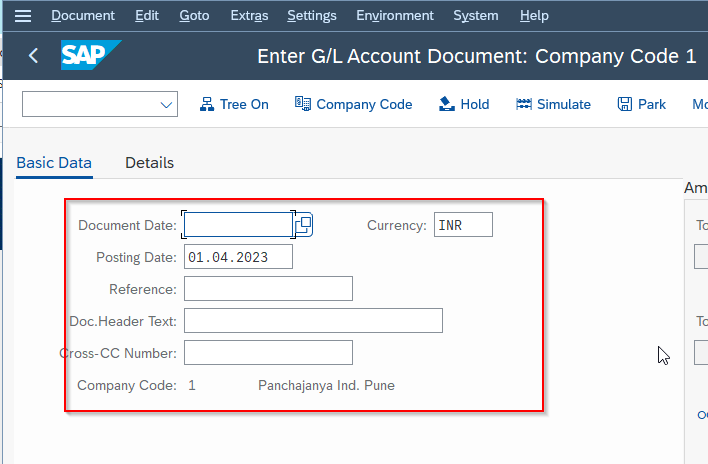
To make the document assignment, click the Post button.
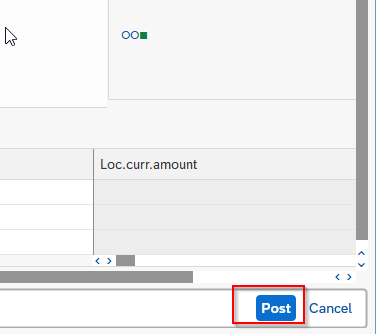
The account assignment is now defined and can be used for tracking expenses and revenues at a granular level in SAP FICO.
- 04 Dec 2013 7:51 am rekha Account assignment is used in Sap Fico if you frequently use the same broad account assignments, such as a distribution of amounts to several company codes, accounts, or cost centers, you can use the account assignment model method to save input time and avoid input errors. The use of account assignment models is limited to G/L account items. T-code OK17 is used in the account assignment. If you have CO-FI real-time integration active you need this account assignment.
/support/notes/service/sap_logo.png)
2514206 - Unknown Account assignment as the default account category
You set Unknown account category as the default category in user's attributes. When creating a SC or PO, the Unknown account category is not defaulted. Error message "No account assignment exists; enter an account assignment" is triggered and you cannot change to another account category.
Environment
- SAP enhancement package 2 for SAP Supplier Relationship Management 7.0
- SAP enhancement package 3 for SAP Supplier Relationship Management 7.0
- SAP enhancement package 4 for SAP Supplier Relationship Management 7.0
- Customizing switch SRM_702_ACCOUNT_ASSIGNMENT is active
EBP, SRMSTD, Unknown, Default settings, PPOMA_BBP, BBP_SC_MODIFY_UI, Leading Field, Account Assignment Category, attributes. , KBA , SRM-EBP-CA-ACC , Account Assignment , Problem
About this page
Search for additional results.
Visit SAP Support Portal's SAP Notes and KBA Search .
Privacy | Terms of use | Legal Disclosure | Copyright | Trademark

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The default account assignment feature suggests default values for specific accounts, improving the accuracy of financial data and streamlining the process through automatic assignment. This reduces the likelihood of errors in manual data entry and saves a considerable amount of time that would otherwise be spent repeatedly assigning these costs.
Default account assignment proposes default values when using specific accounts. It's utilized for automatically directing certain routine transactions to specific account assignment objects, such as posting office expenses to cost centers. Validation is used as an automated checking tool ensuring financial data meets predefined conditions. If ...
This wiki site describes the default account assignment determination process and the related special scenario. Overview. The default account assignment determination has two parts. First the system determine the default accounting category and fill the leading accounting field for the category based on the PPOMA attributes of the user.
The Default Account Assignments for General Ledger Accounts activity is not relevant for general business transactions. For business transaction postings G/L Accounts are derived based on the relevant sub-ledger account determination groups. In SAP Business ByDesign the only option to directly select a G/L account in a posting is by creating a ...
You can create a default account assignment for any cost element using Transaction code OKB9. Later, you can also post a document to check if that account assignment works. Transaction code - OKB9. Step 1 − To create a new Account Assignment, click New Entries. Step 2 − In the next window, you have to enter the following fields −
The activation of Public Sector Management in SAP S/4HANA Cloud requires business transactions with unique PSM account assignments to be posted. A selection of posting factors is predefined by SAP according to the business transaction involved. ... Using the Manage Cost Centers app, you can define default values for the PSM account assignment ...
How to Define Account Assignment? Please follow the steps below to define the account assignment: Execute t-code OKB9 in the SAP command field as shown in the image below. On Change View "Default account assignment": Overview you will see the list of default account assignments. Next, click the New Entries button to create a new account assignment.
Default Account Assignment in SAP CO OKB9 Setting | SAP FICO Tutorial | SAP FICO TrainingCOST ELEMENT: https://youtu.be/sluEwZHYADESome of the handpicked Int...
Learn how to configure and use automatic SAP CO account assignment for external accounting postings in FI, MM and SD modules. Find out the prerequisites, settings, substitutions and default account assignments for different levels and scenarios.
EBP, SRMSTD, Unknown, Default settings, PPOMA_BBP, BBP_SC_MODIFY_UI, Leading Field, Account Assignment Category, attributes. , KBA , SRM-EBP-CA-ACC , Account Assignment , Problem About this page This is a preview of a SAP Knowledge Base Article.