- Login / Sign Up

Believe that journalism can make a difference
If you believe in the work we do at Vox, please support us by becoming a member. Our mission has never been more urgent. But our work isn’t easy. It requires resources, dedication, and independence. And that’s where you come in.
We rely on readers like you to fund our journalism. Will you support our work and become a Vox Member today?
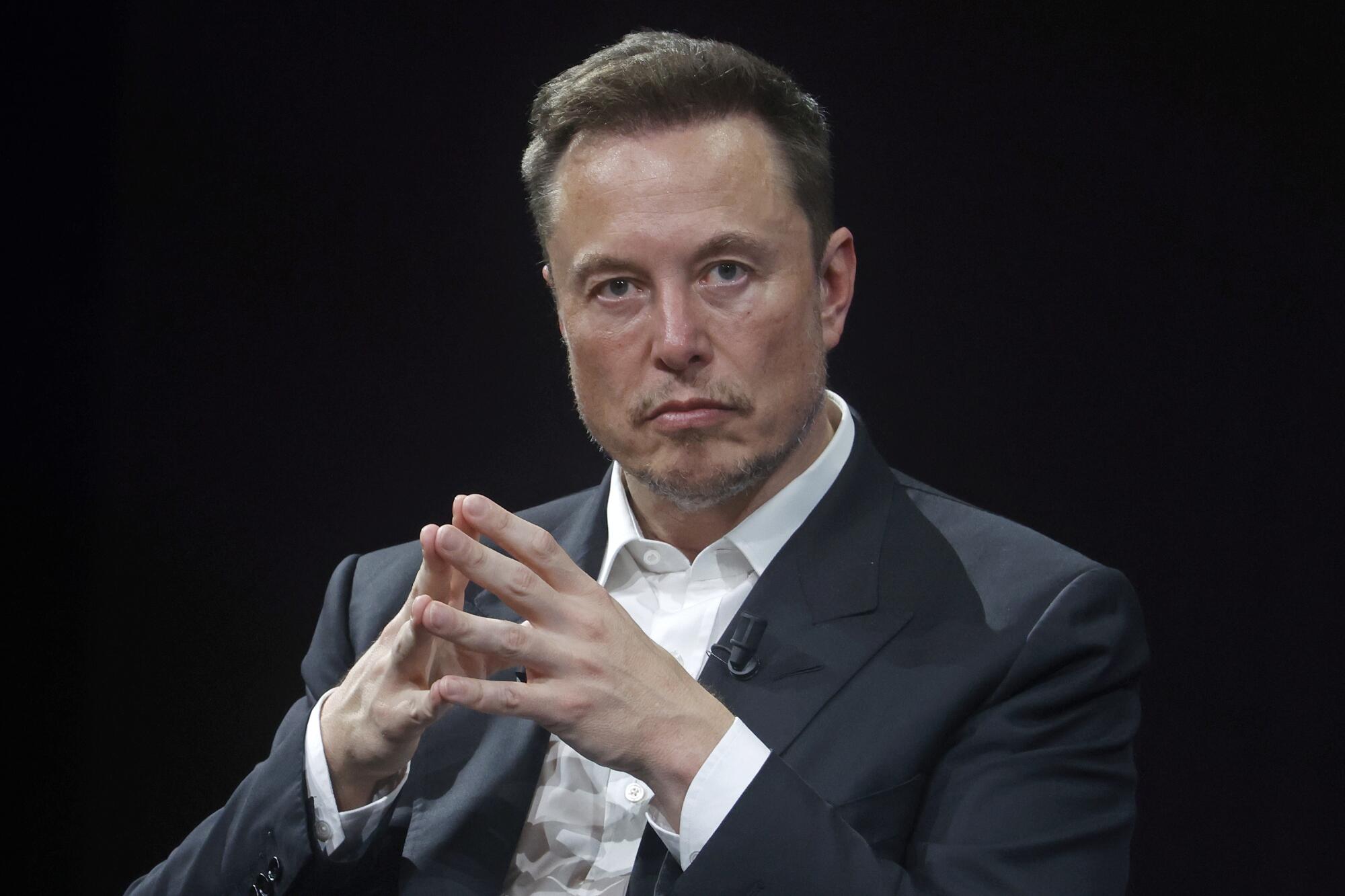
The big Elon Musk biography asks all the wrong questions
In Walter Isaacson’s buzzy new biography, Elon Musk emerges as a callous, chaos-loving man without empathy.
by Constance Grady

There’s a recurring phrase in Walter Isaacson’s new biography Elon Musk . Certain things, Isaacson writes again and again in his dense and thoroughly reported book, are simply “in Musk’s nature,” while others are “not in his nature.” This is a book in which Elon Musk — the richest man in history and surely one of the most infuriating, too — is driven by an immovable internal essence that no one can alter, least of all Musk himself.
Things that are in Musk’s nature according to Isaacson: the desire for total control; obsession; resistance to rules and regulations; insensitivity; a love of drama and chaos and urgency.
Things that are not in Musk’s nature according to Isaacson: deference; empathy; restraint; the ability to collaborate; the instinct to think about how the things he says impact the people around him; doting on his children; vacations.
“He didn’t have the emotional receptors that produce everyday kindness and warmth and a desire to be liked. He was not hardwired to have empathy,” Isaacson writes. “Or, to put it in less technical terms, he could be an asshole.”
The great question of Isaacson’s book is more or less the same question he posed in his 2011 biography of Steve Jobs : Is the innovation worth the assholery? Can we excuse Jobs’s cruelty to his partner Steve Wozniak because we have the iPhone? Can we excuse Musks’s many sins — his capricious firings, his callousness, his willingness to move fast and break things even when the things that get broken are human lives — because after all, he opened up the electric car market and reinvigorated the possibility for American space travel? Is it okay that Musk is an asshole if he’s also accomplishing big things?
“Would a restrained Musk accomplish as much as a Musk unbound?” Isaacson muses in the final sentences of the book. “Could you get the rockets to orbit or the transition to electric vehicles without accepting all aspects of him, hinged and unhinged? Sometimes great innovators are risk-seeking man-children who resist potty training.”
A hundred pages earlier, Isaacson depicted the man he describes as “resisting potty training” personally making the call that Ukraine should cede Crimea to Russia and on those grounds declining to extend satellite services to the Ukrainian military in the disputed territory.
“Risk of WW3 becomes very high,” Musk explained in a private exchange with Ukraine’s Vice Prime Minister Mykhailo Fedorov.
“We look through the eyes of Ukrainians,” Fedorov responded, “and you from the position of a person who wants to save humanity. And not just wants, but does more than anybody else for this.”
The risk-seeking man-child has amassed the power to have world leaders fawn over his unilateral judgment.
Isaacson portrays Musk as someone who loves chaos and has no empathy
Elon Musk was born in Pretoria, South Africa, in 1971. His mother was a model who spent most of her time at work; his father was an engineer and a wheeler-dealer with a violent temper. They sent Elon to nursery school when he was 3 because he seemed intelligent.
Musk was not, however, socially gifted. Isolated and friendless, he was prone to calling his peers stupid, at which point they would beat him up. He took refuge reading his father’s encyclopedia, plus comic books and science fiction novels about single-minded heroes who saved mankind.
For Isaacson, all this is the kind of foreshadowing biographers dream of. Most foreboding is the existence of Musk’s father, Errol, who Isaacson describes as having a “Jekyll and Hyde personality” that mirrors Musk’s own.
“One minute he would be super friendly,” says Elon’s brother Kimbal of Errol, “and the next he would be screaming at you, lecturing you for hours — literally two or three hours while he forced you to just stand there — calling you worthless, pathetic, making scarring and evil comments, not allowing you to leave.”
From Errol, Isaacson intimates, Musk inherited his explosive temper and fondness for dismissing anything that displeases him as stupid. He also learned to crave crisis, to the point that decades later, as CEO of six companies, he would develop a practice of arbitrarily picking one of those companies to send into panic mode. A rule he makes his executives intone like a religious litany is to “work with a maniacal sense of urgency.”
Another one of Musk’s rules is that empathy is not an asset, largely because he himself claims not to experience it. For Isaacson, this is one of the other foundations of Musk’s character, part of that unchangeable nature that was created by the mingled forces of Musk’s traumatic childhood and his neurodivergence. The lack of empathy, he argues, is hardwired in, probably due to the condition Musk describes as Asperger’s. (Asperger’s syndrome is a form of autism spectrum disorder that is no longer an official diagnosis . Musk is self-diagnosed.)
Studies suggest that people with autism actually experience just as much affective empathy as neurotypical people , but that is not a possibility either Musk or Isaacson ever discuss. For the narrative of this book, Musk’s callousness must be something beyond his control, one of the fundamental differences that sets him apart from the kinder, smaller people who make up the rest of the human race.
Musk goes through companies as rapidly as he goes through women
After high school, Musk fled: first to Canada, where his mother was born, and next to America. Over two years at Queen’s University and two at Penn, he earned a dual degree: in physics, so he could work as an engineer with an understanding of the fundamentals, and in business, so he would never have to work for anyone but himself. Upon graduating, he turned down a spot at Stanford’s PhD program to start his first business, an early online business directory called Zip2.
At Zip2, we see the beginnings of Musk’s maniacal work ethic take hold — that, and his inability to work well with others. He and his brother Kimbal sleep on futons in their office and shower at the Y down the street. When new engineers come in, Musk devotes extra time to “fixing their stupid fucking code.” He and Kimbal get into physical knockdown fights in the office; once, Musk has to go to the hospital for a tetanus shot after Kimbal bites him. They sell the company after two years for $300 million.
Zip2 establishes the pattern that will follow Musk throughout his professional career. He works exceptionally long hours, frequently camping out in his office, and he rages at anyone who does not. He tends to dismiss all his collaborators as stupid and will get into furious fights with them (albeit mostly not physical). He will end up having alienated a lot of people, created a pretty interesting product, and made a hell of a lot of money.
From Zip2, Musk moved on to X.com, an early online banking company. Musk had grand plans of using X.com to reinvent banking writ large, but he was pushed out when X merged with PayPal to develop a product he saw, disgustedly, as niche.
Licking his wounds, Musk decided that he would focus his energies only on companies that were truly changing the world. To make humankind an interplanetary species, in 2001 he founded SpaceX, with a mission of bringing humans to Mars. To help stave off the worst of climate change, in 2003 he brought together a group of engineers working on the electric car to amp up the fledgling company that was Tesla.
As Isaacson is always noting, it was not in Musk’s nature to give up control. After briefly experimenting with having other CEOs, he took personal control of both SpaceX and Tesla. Today, he’s CEO of six companies. In addition to Tesla and SpaceX, he’s got the Boring Company (for tunnels), Neuralink (for technology that can interface between human brains and machines), X (formerly known as Twitter), and X.AI, an artificial intelligence company he founded earlier this year. Musk goes through companies fast.
He also goes through women. Isaacson chronicles the four major romantic relationships of Musk’s adult life with a shamelessly misogynistic binary. All Musk’s girlfriends in this book are either devils or angels, and accordingly they bring out either the devil or angel in Musk’s uncontrollable nature.
His college girlfriend and first wife, fantasy novelist Justine Wilson, is one of the devils: “She has no redeeming features,” insists Musk’s mother. Per Isaacson, she thrives on drama and brings out Musk’s control freak side. He pushes her to dye her hair platinum blonde and act the part of the new millionaire’s trophy wife. “I am the alpha in this relationship,” he whispers into her ear as they dance on their wedding night.
Musk’s second wife, the English actress Talulah Riley, is meanwhile an angel. She dotes on Musk’s children with Justine, tells the press she sees it as her job to keep Musk from going “king-crazy,” and throws him elaborate theatrical parties. “If he had liked stability more than storm and drama,” Isaacson writes, “she would have been perfect for him.”
It goes on like that. Actress Amber Heard, who Musk dates for a tumultuous year after divorcing Riley, is a devil who “drew him into a dark vortex.” Musician Grimes, with whom he has three children, is an angel, “chaotic good” to Heard’s “chaotic evil.” (Musk repays her chaotic goodness by secretly fathering more children with one of Neuralink’s executives, a friend of Grimes’s, at the same time that he and Grimes are working with a surrogate to have their second child.) The idea that it might be Musk’s responsibility to control his nature, rather than the responsibility of his romantic partners, appears nowhere in this book.
The book’s big problem is that it ignores systemic problems for individual
In 2018, Musk became the richest man in the world and Time’s Person of the Year. From there he spiraled. His political views veered sharply to the right wing and paranoid. His tweets got weirder. Then he outright bought Twitter and commenced polarizing an already polarized user base. He’s still making the rockets that supply the International Space Station and he’s still building the most successful electric car in the world, but his reputation has taken a palpable hit.
In Isaacson’s narrative, Musk’s social downfall is part of his Shakespearean hubris, the tragic flaw that drives him to continually inflict pain on himself: the lack of empathy coupled with the craving for excitement; the genuine intelligence matched by over-the-top arrogance. It drives him to achieve great things and to mess up badly.
For Isaacson, this binary illustrates why Musk’s acquisition of Twitter was destined for trouble. “He thought of it as a technology company” within his realm of expertise, Isaacson writes, and didn’t understand that it was “an advertising medium based on human emotions and relationships,” and thus well outside his lane. What does the man who doesn’t believe in empathy know about connecting human beings to one another? But how could the man who needs chaos to function resist the internet’s most visibly chaotic platform?
That’s a genuine insight, but by and large, Isaacson’s focus in this book is not on analysis. Elon Musk is strictly a book of reportage, based on the two years Isaacson spent shadowing Musk and the scores of interviews he did with Musk’s associates. His reporting is rigorous and dogged; you can see the sweat on the pages. If his prose occasionally clunks (Isaacson cites the “feverish fervor” of Musk’s fans and critics), that’s not really the point of this kind of book. Instead, Isaacson’s great weakness shows itself in his blind spots, in the places where he declines to train his dutiful reporter’s eye.
Isaacson spends a significant amount of page time covering one of Musk’s signature moves: ignoring the rules. Part of the “algorithm” he makes his engineers run on every project involves finding the specific person who wrote each regulation they slam up against as they build and then interrogating the person as to what the regulation is supposed to do. All regulations are believed by default to be “dumb,” and Musk does not accept “safety” as a reason for a regulation to exist.
At one point, Isaacson describes Musk becoming enraged when, working on the Tesla Model S, he finds a government-mandated warning about child airbag safety on the passenger-side visor. “Get rid of them,” he demands. “People aren’t stupid. These stickers are stupid.” Tesla faces recall notices because of the change, Isaacson reports, but Musk “didn’t back down.”
What Isaacson doesn’t mention is that Musk consistently ignores safety regulations whenever they clash with his own aesthetic sense, to consistently dangerous results.
According to a 2018 investigation from the Center for Investigative Reporting’s Reveal , Musk demanded Tesla factories minimize the auto industry standard practice of painting hazard zones yellow and indicating caution with signs and beeps and flashing lights, on the grounds he doesn’t particularly care for any of those things. As a result, Tesla factories mostly distinguish caution zones from other zones with different shades of gray.
Isaacson does report that Musk removed safety sensors from the Tesla production lines because he thought they were slowing down the work, and that his managers worried that his process was unsafe. “There was some truth to the complaints,” Isaacson allows. “Tesla’s injury rate was 30 percent higher than the rest of the industry.” He does not report that Tesla’s injury rate is in fact on par with the injury rate at slaughterhouses, or that it apparently cooked its books to cover up its high injury rate .
Isaacson is vague about exactly what kind of injuries occur in the factories Musk runs. Nowhere does he mention anything along the lines of what Reveal reports as Tesla workers “sliced by machinery, crushed by forklifts, burned in electrical explosions, and sprayed with molten metal.” He notes that Musk violated public safety orders to keep Tesla factories open after the Covid-19 lockdown had begun, but claims that “the factory experienced no serious Covid outbreak.” In fact, the factory Musk illegally opened would report 450 positive Covid cases .
No one can accuse the biographer who frankly admits that his subject is an asshole of ignoring his flaws. Yet Isaacson does regularly ignore the moments at which Musk’s flaws scale . He has no interest in the many, many times when Musk did something mavericky and counterintuitive and, because of his power and wealth and platform and reach, it ended up hurting a whole lot of people.
Instead, Isaacson seems most interested in Musk’s cruelty when it’s confined to the level of the individual. He likes the drama of Musk telling his cousin that his solar roof prototype is “total fucking shit” and then pushing him out of the company, or of Musk scrambling to fire Twitter’s executive team before they can resign so he doesn’t have to pay out their severance packages. Those are the moments of this book with real juice to them.
Ultimately, it’s this blind spot that prevents Isaacson from fully exploring the question at the core of Elon Musk : Is Elon Musk’s cruelty worth it since he’s creating technology that might change the world? Because Isaacson is only interested in Musk’s cruelty when it’s personal, in this book, that question looks like: If SpaceX ends up taking us all to Mars and saving humanity, will it matter that Musk was really mean to his cousin?
Widen the scope, and the whole thing becomes much more interesting and urgent. If Elon Musk consistently endangers the people who work for him and the people who buy his products and the people who stand in his way, does it matter if he thinks he’s saving the human race?
Isaacson compares Musk to a “man-child who resists potty-training.” If we look closely at the amount of damage he is positioned to do, how comfortable are we with the power Elon Musk currently has?
Correction, September 15, 11:30 am: A previous version of this story misstated a university Musk attended. It is Queen’s University.
Most Popular
- You’re being lied to about “ultra-processed” foods
- House Republicans just exposed the limits of Trump’s power
- Everyone’s favorite frustrating, hard-to-clean, potentially dangerous household device
- Take a mental break with the newest Vox crossword
- Why is money so hard?
Today, Explained
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
This is the title for the native ad
More in Culture

The surprising power of podcasts.

And why so many of them are shot in Vancouver.

Could a movie musical about a trans Mexican drug lord be this awards season’s Crash?

Welcome to the hair transplant capital of the world

The Taiwan invasion everyone fears might never happen. Here’s what could take place instead.

It sends an important message, but may not translate to an immediate fix.
Let’s put a stake in the ‘great man’ biography — starting with Isaacson’s ‘Elon Musk’

- Copy Link URL Copied!
By Walter Isaacon Simon & Schuster: 688 pages, $35 If you buy books linked on our site, The Times may earn a commission from Bookshop.org , whose fees support independent bookstores.
The opening pages of “Elon Musk,” the new doorstop biography from Walter Isaacson , the bestselling chronicler of the great innovative men of modern history, are jarring, especially to anyone expecting to be greeted with plucky tales of unlikely genius.
On the first page, we’re told that Musk, the CEO of Tesla and SpaceX, owner of X (formerly Twitter), and currently the world’s richest man, was born into a land of incredible violence in South Africa , “with machine gun attacks and knife killings common,” where boys have to “wade through pools of blood” on the way to concerts and are sent to wilderness camps that resemble “a paramilitary Lord of the Flies,” per Musk. Young Elon is bullied relentlessly — by his classmates but also by his abusive father — until he grows big enough to fight back.
Introducing the 688-page biography this way seems designed to address Musk’s recent turn toward combativeness and cruelty — if not justifying it, then offering a skeleton key to understanding where it’s rooted. But as we learn throughout the book, the Musks are persistent fabulists, prone to embellishment and fabrication, and this becomes the first of many narrative sequences that the reader must consider with an eye to truth versus narrative convenience.

The biggest ideas and pettiest rages in Walter Isaacson’s Elon Musk biography
Walter Isaacson’s biography of Elon Musk distilled, from fierce mood swings and Ukraine intervention to his ‘dumb’ Pelosi tweet and that time he had the 405 repainted.
And Isaacson’s truth is, above all, selective. Given Musk’s recent coziness with white nationalists and peddlers of junk race science and his ongoing tirade against the Anti-Defamation League , whom he blames (rather than himself) for chasing advertisers from Twitter, it seems startling that nothing in those opening pages touches on his experiences with apartheid . Much of that horrendous violence unfolding in 1980s South Africa was precipitated by a brutally racist government; we discover only that it taught Musk to survive adversity. “My pain threshold is very high,” he tells Isaacson.
We do learn that Musk’s Canadian grandfather was involved in a fringe political party with antisemitic views and relocated his family to South Africa because he liked the government better — he is described as harboring “quirky conservative views” — and that Musk’s father is now outspokenly racist. But in a book that goes to great lengths to dissect the transmission of habits and ideas from father and son, Elon is allowed to stay mum.

Silences like that come to haunt the capacious hull of “Elon Musk” — to the point that they risk drowning out the project altogether.
After the burst of violence in the introduction, we move into more familiar territory, led on by Isaacson’s brisk, propulsive prose: Musk is a spacy, lonely outsider who is bright but has trouble making friends. He disappears into video games and science fiction and soon dreams of horizons far beyond his hometown, and sets out to North America with an entrepreneurial spirit in tow. He graduates with a dual degree in physics and economics from the University of Pennsylvania, gets accepted into a PhD program at Stanford, but decides instead to set out into the buzzing startup scene of Silicon Valley.
He founds Zip2 with his brother Kimbal , sells it , and makes a lot of money. He founds the first iteration of X.com, merges with PayPal, and makes even more. Initially the CEO of both companies, he’s pushed out of each — in a bit of foreshadowing, Musk is booted from PayPal because of his monomaniacal dedication to the porn-adjacent letter X, as well as the idea that PayPal should try to “take over the world’s financial system.” His dismissal, brought about in a coup led by Peter Thiel and other members of the so-called PayPal mafia, leaves him with a large pool of cash, an ax or two to grind and an aspiration to take on loftier goals.

What drove Elon Musk — onetime Democratic ‘fanboy’ — to troll progressive politics
In his ‘Elon Musk’ biography, Walter Isaacson examines the billionaire’s political evolution, from fundraising for Democrats to trolling progressive politicians.
Here the limitations of Isaacson’s project are revealed: Musk had pushed some of the worst ideas of his young career. From a business perspective, it seemed his colleagues were correct to oust him, preserve their product and make them all fabulously wealthy in an IPO and later sale to EBay . But here’s Isaacson’s diagnosis: “He was a visionary who didn’t play well with others.” The word “visionary,” in this application, is doing a lot of work.
The narrative is filled with moments of similar dissonance, with Isaacson quick to praise Musk’s incessant risk-taking after a disaster, or to excuse his rude behavior to underlings as necessary to get things done, or to nod along in prose while Musk announces his latest idea that will transform the world. He does occasionally push back, as when Musk claims the Hyperloop will change everything (“It did not change everything”), but Isaacson mostly accepts Musk’s confident prognostications as gospel.
Isaacson — biographer of Steve Jobs , Albert Einstein , Henry Kissinger , Benjamin Franklin — is concerned with the study of world-moving men (and occasionally a woman ). What makes innovators tick? What makes them so successful? (In the case of Musk, the prognosis can be summarized as: a large appetite for risk, a willingness to alienate colleagues, a detailed knowledge of industry and science, an ability to process work tasks like an algorithm and a predilection for drawing lessons from video games and “ The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy . ”)
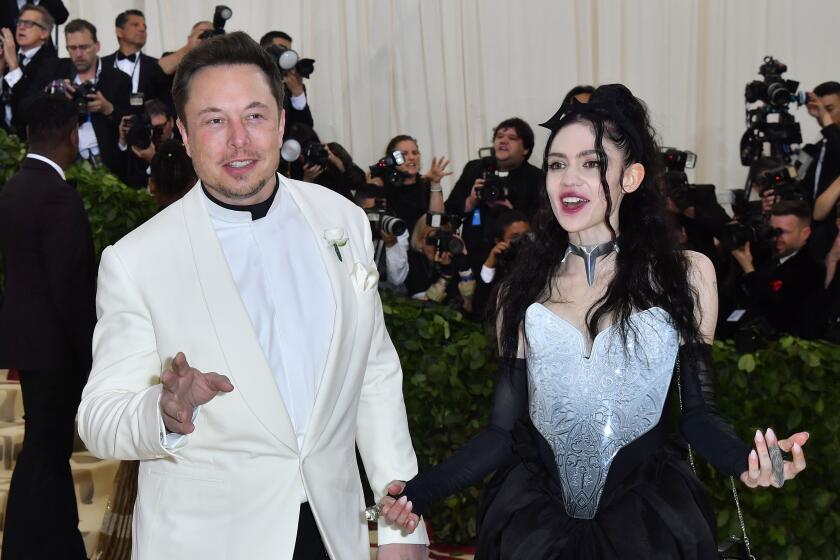

Elon Musk confirms he and Grimes privately welcomed a third child, Techno Mechanicus
Elon Musk and Grimes have a third child named Techno Mechanicus, the tech mogul confirmed ahead of the release of Walter Isaacson’s forthcoming biography.
This sort of framing may have made sense in the early aughts, when so many were dizzy with optimism that Amazon’s everything store and the iPhone would transform the world for the better. It makes less sense 12 years after “ Steve Jobs ” — now that we’ve seen the toll the tech giants have levied on society: labor exploitation at Amazon, Uber and, yes, Tesla; misinformation and harassment on social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram and, yes, Twitter. These costs are almost entirely omitted from the equation of “Elon Musk.”
That may be because there is a tacit pact between author and subject in the Isaacson “great man” biography: The author will unearth unflattering personal anecdotes and share stories about the subject’s capacity to be cruel. In exchange, the subject’s greatness will be treated as an assumption, the raison d’etre for the book itself. In honor of Isaacson’s habit of using pithy, memorable phrases to describe a phenomenon, we might call it “the Isaacson Accord.”

And so it is in “Elon Musk,” whose subject is described as “a visionary” and a “risk-taking innovator” and, most pointedly, “the one launching us toward Mars and an electric-vehicle future.” Musk’s many fans will surely take those descriptors as a given. But that seems all the more reason to challenge the assumptions. Because the Isaacson Accord turns out to be a devil’s bargain. We get a lot of palace intrigue, well-told anecdotes and some genuine insight into Musk’s familial psychology; but the good stuff almost comes in spite of Isaacson’s constant framing of Musk as a moody but brilliant world-mover.
Worse, in exchange for unprecedented access, the Isaacson Accord demands that a lot of the most difficult and pressing questions go unasked and, therefore, unanswered.
Isaacson repeatedly says one of Musk’s unparalleled strengths as a manager is his intimate knowledge of the factory floors where his products are made. Yet there is not a single mention of the sweeping allegations of racial discrimination at Tesla’s flagship Fremont factory that resulted in juries finding Tesla liable for millions in damages. Workers of color say they were called the N-word and saw swastikas painted on the bathroom. In 2021, Tesla was ordered to pay $137 million to one employee who suffered racist abuse, though that amount was later reduced.

Walter Isaacson brings ‘Elon Musk’ to book club this fall
L.A. Times Book Club lineup features Elon Musk biographer Walter Isaacson and Christian Cooper, author of ‘Better Living Through Birds.”
Likewise, there is no examination of the union drives at Tesla plants, or the wrongful termination case Tesla lost after firing a worker involved in organizing. In all the discussion of Tesla’s self-driving Autopilot program, there is no mention of the blockbuster revelation from a former engineer that one of the first key promotions of Autopilot was staged , contributing to the false sense of security buyers had in the program.
And while a major focus of the book is the impact of Musk’s abusive father and the traits that might have been passed down, Isaacson speeds past any explanation of the falling out with Musk’s trans daughter, Jenna , allowing Musk to file it away as her political views simply having grown too radical. Isaacson does not list her as a source in the book, as her twin brother, and does not say whether he tried to reach out. Musk’s story, about Jenna having succumbed to the “woke mind virus,” stands.
No biography can or should be totally comprehensive, but it’s pretty easy to conclude which sorts of topics and conversations Isaacson decided it would be best to avoid altogether. I started “Elon Musk” wondering if the world needed another book positioning Musk as a great man — Ashlee Vance’s book of the same title ably covered many of the same bases — and finished thinking it’s time to retire the entire genre of “great innovator” biographies, period.
The idea that the future is created by flawed geniuses who happen to accumulate great wealth is outmoded and simplistic, and it encourages a flattened view of how technology is developed and whom it impacts. Just scan the list of sources Isaacson includes in the book: executives, venture capitalists, founders and high-ranking engineers. Yes, Isaacson spoke to “adversaries” like Jeff Bezos and Bill Gates, but not (at least per the list) to line workers, not to Jenna, not to anyone whose family member died in an Autopilot crash, nor anyone who tried to organize a Tesla plant.
The bottom line: This is the story Musk himself wants told. Sure, he might have excluded a handful of the details that proved personally embarrassing, but nothing here challenges the idea that Elon Musk is an all-too-human hero valiantly trying to save humanity from the threats he sees cascading down upon us. It’s the book Musk would have written himself.
More to Read

Billionaire who performed the first private spacewalk is Trump’s pick to lead NASA


Musk has Trump’s ear, and that could help Tesla. Other EV makers? Maybe not so much

What to know about Elon Musk’s contracts with the federal government
Sign up for our Book Club newsletter
Get the latest news, events and more from the Los Angeles Times Book Club, and help us get L.A. reading and talking.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.

Brian Merchant was the Los Angeles Times’ technology columnist. He’s the author of “The One Device: The Secret History of the iPhone” and the forthcoming “Blood in the Machine: The Origins of the Rebellion Against Big Tech.” Merchant is the co-founder of Terraform, Vice Media’s speculative fiction website, and the co-editor of the anthology “Terraform: Watch/Worlds/Burn.” Previously, he was a senior editor at Motherboard, and his writing has appeared in the New York Times, Harper’s Magazine, WIRED, the Atlantic, Fast Company, and Slate, among others.
More From the Los Angeles Times

Entertainment & Arts
Mystery writers reveal their go-to books for holiday gift-giving

Opinion: Conflict in South Korea reopens the very wounds examined in this year’s Nobel laureate’s work

The week’s bestselling books, Dec. 22

As children’s book bans soar, sales are down and librarians are afraid. Even in California
Most read in books, the week’s bestselling books, dec. 15.

In 2021, Elon Musk became the world’s richest man (no woman came close), and Time named him Person of the Year: “This is the man who aspires to save our planet and get us a new one to inhabit: clown, genius, edgelord, visionary, industrialist, showman, cad; a madcap hybrid of Thomas Edison, P. T. Barnum, Andrew Carnegie and Watchmen ’s Doctor Manhattan, the brooding, blue-skinned man-god who invents electric cars and moves to Mars.” Right about when Time was preparing that giddy announcement, three women whose ovaries and uteruses were involved in passing down the madcap man-god’s genes were in the maternity ward of a hospital in Austin. Musk believes a declining birth rate is a threat to civilization and, with his trademark tirelessness, is doing his visionary edgelord best to ward off that threat. Shivon Zilis, a thirty-five-year-old venture capitalist and executive at Musk’s company Neuralink, was pregnant with twins, conceived with Musk by in-vitro fertilization, and was experiencing complications. “He really wants smart people to have kids, so he encouraged me to,” Zilis said. In a nearby room, a woman serving as a surrogate for Musk and his thirty-three-year-old ex-wife, Claire Boucher, a musician better known as Grimes, was suffering from pregnancy complications, too, and Grimes was staying with her.
“I really wanted him to have a daughter so bad,” Grimes said. At the time, Musk had had seven sons, including, with Grimes, a child named X. Grimes did not know that Zilis, a friend of hers, was down the hall, or that Zilis was pregnant by Musk. Zilis’s twins were born seven weeks premature; the surrogate delivered safely a few weeks later. In mid-December, Grimes’s new baby came home and met her brother X. An hour later, Musk took X to New York and dandled him on his knee while being photographed for Time .
“He dreams of Mars as he bestrides Earth, square-jawed and indomitable,” the magazine’s Person of the Year announcement read. Musk and Grimes called the baby, Musk’s tenth, Y, or sometimes “Why?,” or just “?”—a reference to Musk’s favorite book, Douglas Adams’s “ The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy ,” because, Grimes explained, it’s a book about how knowing the question is more important than knowing the answer.
Discover notable new fiction and nonfiction.
Elon Musk is currently at or near the helm of six companies: Tesla, SpaceX (which includes Starlink), the Boring Company, Neuralink, X (formerly known as Twitter), and X.AI, an artificial-intelligence company that he founded, earlier this year, because he believes that human intelligence isn’t reproducing fast enough, while artificial intelligence is getting more artificially intelligent exponentially. Call it Musk’s Law: the answer to killer robots is more Musk babies. Plus, more Musk companies. “I can’t just sit around and do nothing,” Musk says, fretting about A.I., in Walter Isaacson’s new biography, “ Elon Musk ” (Simon & Schuster), a book that can scarcely contain its subject, in that it raises infinitely more questions than it answers.
“Are you sincerely trying to save the world?” Stephen Colbert once asked Musk on “The Late Show.” “Well, I’m trying to do good things, yeah, saving the world is not, I mean . . . ,” Musk said, mumbling. “But you’re trying to do good things, and you’re a billionaire,” Colbert interrupted. “Yeah,” Musk said, nodding. Colbert said, “That seems a little like superhero or supervillain. You have to choose one.” Musk paused, his face blank. That was eight years, several companies, and as many children ago. Things have got a lot weirder since. More Lex Luthor, less Tony Stark.
Musk controls the very tiniest things, and the very biggest. He oversees companies, valued at more than a trillion dollars, whose engineers have built or are building, among other things, reusable rocket ships, a humanoid robot, hyperloops for rapid transit, and a man-machine interface to be implanted in human brains. He is an entrepreneur, a media mogul, a political provocateur, and, not least, a defense contractor: SpaceX has received not only billions of dollars in government contracts for space missions but also more than a hundred million dollars in military contracts for missile-tracking satellites, and Starlink’s network of four thousand satellites— which provides Pentagon-funded services to Ukraine —now offers a military service called Starshield. Day by day, Musk’s companies control more of the Internet, the power grid, the transportation system, objects in orbit, the nation’s security infrastructure, and its energy supply.
And yet. At a jury trial earlier this year, Musk’s lawyer repeatedly referred to his client, a middle-aged man, as a “kid.” The Wall Street Journal has described him as suffering from “tantrums.” The Independent has alleged that selling Twitter to Musk was “like handing a toddler a loaded gun.”
“I’m not evil,” Musk said on “Saturday Night Live” a couple of years ago, playing the dastardly Nintendo villain Wario, on trial for murdering Mario. “I’m just misunderstood.” How does a biographer begin to write about such a man? Some years back, after Isaacson had published a biography of Benjamin Franklin and was known to be writing one of Albert Einstein, the Apple co-founder Steve Jobs called him up and asked him to write his biography; Isaacson says he wondered, half jokingly, whether Jobs “saw himself as the natural successor in that sequence.” I don’t think Musk sees himself as a natural successor to anyone. As I read it, Isaacson found much to like and admire in Jobs but is decidedly uncomfortable with Musk. (He calls him, at one point, “an asshole.”) Still, Isaacson’s descriptions of Jobs and Musk are often interchangeable. “His passions, perfectionism, demons, desires, artistry, devilry, and obsession for control were integrally connected to his approach to business and the products that resulted.” (That’s Jobs.) “It was in his nature to want total control.” (Musk.) “He didn’t have the emotional receptors that produce everyday kindness and warmth and a desire to be liked.” (Musk.) “He was not a model boss or human being.” (Jobs.) “This is a book about the roller-coaster life and searingly intense personality of a creative entrepreneur whose passion for perfection and ferocious drive revolutionized six industries.” I ask you: Which?
“Sometimes great innovators are risk-seeking man-children who resist potty training,” Isaacson concludes in the last lines of his life of Musk. “They can be reckless, cringeworthy, sometimes even toxic. They can also be crazy. Crazy enough to think they can change the world.” It’s a disconcerting thing to read on page 615 of a biography of a fifty-two-year-old man about whom a case could be made that he wields more power than any other person on the planet who isn’t in charge of a nuclear arsenal. Not potty-trained? Boys will be . . . toddlers?
Elon Musk was born in Pretoria, South Africa, in 1971. His grandfather J. N. Haldeman was a staunch anti-Communist from Canada who in the nineteen-thirties and forties had been a leader of the anti-democratic and quasi-fascist Technocracy movement. (Technocrats believed that scientists and engineers should rule.) “In 1950, he decided to move to South Africa,” Isaacson writes, “which was still ruled by a white apartheid regime.” In fact, apartheid had been declared only in 1948, and the regime was soon recruiting white settlers from North America, promising restless men such as Haldeman that they could live like princes. Isaacson calls Haldeman’s politics “quirky.” In 1960, Haldeman self-published a tract, “The International Conspiracy to Establish a World Dictatorship & the Menace to South Africa,” that blamed the two World Wars on the machinations of Jewish financiers.
Musk’s mother, Maye Haldeman, was a finalist for Miss South Africa during her tumultuous courtship with his father, Errol Musk, an engineer and an aviator. In 2019, she published a memoir titled “A Woman Makes a Plan: Advice for a Lifetime of Adventure, Beauty, and Success.” For all that she writes about growing up in South Africa in the nineteen-fifties and sixties, she never once mentions apartheid.
Isaacson, in his account of Elon Musk’s childhood, barely mentions apartheid himself. He writes at length and with compassion about the indignities heaped upon young Elon by schoolmates. Elon, an awkward, lonely boy, was bored in school and had a tendency to call other kids “stupid”; he was also very often beaten up, and his father frequently berated him, but when he was ten, a few years after his parents divorced, he chose to live with him. (Musk is now estranged from his father, a conspiracist who has called Joe Biden a “pedophile President,” and who has two children by his own stepdaughter; he has said that “the only thing we are here for is to reproduce.” Recently, he warned Elon, in an e-mail, that “with no Whites here, the Blacks will go back to the trees.”)

Link copied
Musk’s childhood sounds bad, but Isaacson’s telling leaves out rather a lot about the world in which Musk grew up. In the South Africa of “Elon Musk,” there are Musks and Haldemans—Elon and his younger brother and sister and his many cousins—and there are animals, including the elephants and monkeys who prove to be a nuisance at a construction project of Errol’s. There are no other people, and there are certainly no Black people, the nannies, cooks, gardeners, cleaners, and construction workers who built, for white South Africans, a fantasy world. And so, for instance, we don’t learn that in 1976, when Elon was four, some twenty thousand Black schoolchildren in Soweto staged a protest and heavily armed police killed as many as seven hundred. Instead, we’re told, “As a kid growing up in South Africa, Elon Musk knew pain and learned how to survive it.”
Musk, the boy, loved video games and computers and Dungeons & Dragons and “The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy,” and he still does. “I took from the book that we need to extend the scope of consciousness so that we are better able to ask the questions about the answer, which is the universe,” Musk tells Isaacson. Isaacson doesn’t raise an eyebrow, and you can wonder whether he has read “Hitchhiker’s Guide,” or listened to the BBC 4 radio play on which it is based, first broadcast in 1978. It sounds like this:
Far back in the mists of ancient time, in the great and glorious days of the former galactic empire, life was wild, rich, and, on the whole, tax free. . . . Many men of course became extremely rich, but this was perfectly natural because no one was really poor, at least, no one worth speaking of.
“The Hitchhiker’s Guide” is not a book about how “we need to extend the scope of consciousness so that we are better able to ask the questions about the answer, which is the universe.” It is, among other things, a razor-sharp satiric indictment of imperialism:
And for these extremely rich merchants life eventually became rather dull, and it seemed that none of the worlds they settled on was entirely satisfactory. Either the climate wasn’t quite right in the later part of the afternoon or the day was half an hour too long or the sea was just the wrong shade of pink. And thus were created the conditions for a staggering new form of industry: custom-made, luxury planet-building.
Douglas Adams wrote “The Hitchhiker’s Guide” on a typewriter that had on its side a sticker that read “End Apartheid.” He wasn’t crafting an instruction manual for mega-rich luxury planet builders.
Biographers don’t generally have a will to power. Robert Caro is not Robert Moses and would seem to have very little in common with Lyndon the “B” is for “bastard” Johnson. Walter Isaacson is a gracious, generous, public-spirited man and a principled biographer. This year, he was presented with the National Humanities Medal. But, as a former editor of Time and a former C.E.O. of CNN and of the Aspen Institute, Isaacson also has an executive’s affinity for the C-suite, which would seem to make it a challenge to keep a certain distance from the world view of his subject. Isaacson shadowed Musk for two years and interviewed dozens of people, but they tend to have titles like C.E.O., C.F.O., president, V.P., and founder. The book upholds a core conviction of many executives: sometimes to get shit done you have to be a dick. He dreams of Mars as he bestrides Earth, square-jawed and indomitable . For the rest of us, Musk’s pettiness, arrogance, and swaggering viciousness are harder to take, and their necessity less clear.
Isaacson is interested in how innovation happens. In addition to biographies of Franklin, Einstein, Jobs, and Leonardo da Vinci , he has also written about figures in the digital revolution and in gene editing. Isaacson puts innovation first: This man might be a monster, but look at what he built! Whereas Mary Shelley, for instance, put innovation second: The man who built this is a monster! The political theorist Judith Shklar once wrote an essay called “ Putting Cruelty First .” Montaigne put cruelty first, identifying it as the worst thing people do; Machiavelli did not. As for “the usual excuse for our most unspeakable public acts,” the excuse “that they are necessary,” Shklar knew this to be nonsense. “Much of what passed under these names was merely princely wilfulness,” as Shklar put it. This is always the problem with princes.
Elon Musk started college at the University of Pretoria but left South Africa in 1989, at seventeen. He went first to Canada and, after two years at Queen’s University in Ontario, transferred to the University of Pennsylvania, where he studied physics and economics, and wrote a senior paper titled “The Importance of Being Solar.” He had done internships in Silicon Valley and, after graduating, enrolled in a Ph.D. program in materials science at Stanford, but he deferred admission and never went. It was 1995, the year the Internet opened to commercial traffic. All around him, frogs were turning into princes. He wanted to start a startup. Musk and his brother Kimball, with money from their parents, launched Zip2, an early online Yellow Pages that sold its services to newspaper publishers. In 1999, during the dot-com boom, they sold it to Compaq for more than three hundred million dollars. Musk, with his share of the money, launched one of the earliest online banking companies. He called it X.com. “I think X.com could absolutely be a multibillion-dollar bonanza,” he told CNN, but, meanwhile, “I’d like to be on the cover of Rolling Stone .” That would have to wait for a few years, but in 1999 Salon announced, “Elon Musk Is Poised to Become Silicon Valley’s Next Big Thing,” in a profile that advanced what was already a hackneyed set of journalistic conventions about the man-boy man-gods of Northern California: “The showiness, the chutzpah, the streak of self-promotion and the urge to create a dramatic public persona are major elements of what makes up the Silicon Valley entrepreneur. . . . Musk’s ego has gotten him in trouble before, and it may get him in trouble again, yet it is also part and parcel of what it means to be a hotshot entrepreneur.” Five months later, Musk married his college girlfriend, Justine Wilson. During their first dance at their wedding, he whispered in her ear, “I am the alpha in this relationship.”
“ Big Ego of Hotshot Entrepreneur Gets Him Into Trouble ” is more or less the running headline of Musk’s life. In 2000, Peter Thiel’s company Confinity merged with X.com, and Musk regretted that the new company was called PayPal, instead of X . (He later bought the domain x.com, and for years he kept it as a kind of shrine, a blank white page with nothing but a tiny letter “x” on the screen.) In 2002, eBay paid $1.5 billion for the company, and Musk drew on his share of the sale to start SpaceX. Two years later, he invested around $6.5 million in Tesla; he became both its largest shareholder and its chairman. Around then, in his Marvel Iron Man phase, Musk left Northern California for Los Angeles, to swan with starlets. Courted by Ted Cruz during COVID , he moved to Texas, because he dislikes regulation, and because he objected to California’s lockdowns and mask mandates.
Musk’s accomplishments as the head of a series of pioneering engineering firms are unrivalled. Isaacson takes on each of Musk’s ventures, venture by venture, chapter by chapter, emphasizing the ferocity and the velocity and the effectiveness of Musk’s management style—“A maniacal sense of urgency is our operating principles” is a workplace rule. “How the fuck can it take so long?” Musk asked an engineer working on SpaceX’s Merlin engines. “This is stupid. Cut it in half.” He pushed SpaceX through years of failures, crash after crash, with the confidence that success would come. “Until today, all electric cars sucked,” Musk said, launching Tesla’s Roadster, leaving every other electric car and most gas cars in the dust. No automotive company had broken into that industry in something like a century. Like SpaceX, Tesla went through very hard times. Musk steered it to triumph, a miracle amid fossil fuel’s stranglehold. “Fuck oil,” he said.
“Comradery is dangerous” is another of Musk’s workplace maxims. He was ousted as PayPal’s C.E.O. and ousted as Tesla’s chairman. He’s opposed to unions, pushed workers back to the Tesla plants at the height of the Covid pandemic—some four hundred and fifty reportedly got infected—and has thwarted workers’ rights at every turn.
Musk has run through companies and he has run through wives. In some families, domestic relations are just another kind of labor relations. He pushed his first wife, Justine, to dye her hair blonder. After they lost their firstborn son, Nevada, in infancy, Justine gave birth to twins (one of whom they named Xavier, in part for Professor Xavier, from “X-Men”) and then to triplets. When the couple fought, he told her, “If you were my employee, I would fire you.” He divorced her and soon proposed to Talulah Riley, a twenty-two-year-old British actress who had only just moved out of her parents’ house. She said her job was to stop Musk from going “king-crazy”: “People become king, and then they go crazy.” They married, divorced, married, and divorced. But “you’re my Mr. Rochester,” she told him. “And if Thornfield Hall burns down and you are blind, I’ll come and take care of you.” He dated Amber Heard, after her separation from Johnny Depp. Then he met Grimes. “I’m just a fool for love,” Musk tells Isaacson. “I am often a fool, but especially for love.”
He is also a fool for Twitter. His Twitter account first got him into real trouble in 2018, when he baselessly called a British diver, who helped rescue Thai children trapped in a flooded cave, a “pedo” and was sued for defamation. That same year, he tweeted, “Am considering taking Tesla private at $420,” making a pot joke. “Funding secured.” (“I kill me,” he says about his sense of humor.) The S.E.C. charged him with fraud, and Tesla stock fell more than thirteen per cent. Tesla shareholders sued him, alleging that his tweets had caused their stock to lose value. On Joe Rogan’s podcast, he went king-crazy, lighting up a joint. He looked at his phone. “You getting text messages from chicks?” Rogan asked. “I’m getting text messages from friends saying, ‘What the hell are you doing smoking weed?’ ”
“Musk’s goofy mode is the flip side of his demon mode,” Isaacson writes. Musk likes this kind of cover. “I reinvented electric cars, and I’m sending people to Mars in a rocket ship,” he said in his “S.N.L.” monologue, in 2021. “Did you think I was also going to be a chill, normal dude?” In that monologue, he also said that he has Asperger’s. A writer in Newsweek applauded this announcement as a “milestone in the history of neurodiversity.” But, in Slate, Sara Luterman, who is autistic, was less impressed; she denounced Musk’s “coming out” as “self-serving and hollow, a poor attempt at laundering his image as a heartless billionaire more concerned with cryptocurrency and rocket ships than the lives of others.” She put cruelty first.
Musk’s interest in acquiring Twitter dates to 2022. That year, he and Grimes had another child. His name is Techno Mechanicus Musk, but his parents call him Tau, for the irrational number. But Musk also lost a child. His twins with Justine turned eighteen in 2022 and one of them, who had apparently become a Marxist, told Musk, “I hate you and everything you stand for.” It was, to some degree, in an anguished attempt to heal this developing rift that, in 2020, Musk tweeted, “I am selling almost all physical possessions. Will own no house.” That didn’t work. In 2022, his disaffected child petitioned a California court for a name change, to Vivian Jenna Wilson, citing, as the reason for the petition, “Gender Identity and the fact that I no longer live with or wish to be related to my biological father in any way, shape or form.” She refuses to see him. Musk told Isaacson he puts some of the blame for this on her progressive Los Angeles high school. Lamenting the “woke-mind virus,” he decided to buy Twitter. I just can’t sit around and do nothing .
Musk’s estrangement from his daughter is sad, but of far greater consequence is his seeming estrangement from humanity itself. When Musk decided to buy Twitter, he wrote a letter to its board. “I believe free speech is a societal imperative for a functioning democracy,” he explained, but “I now realize the company will neither thrive nor serve this societal imperative in its current form.” This is flimflam. Twitter never has and never will be a vehicle for democratic expression. It is a privately held corporation that monetizes human expression and algorithmically maximizes its distribution for profit, and what turns out to be most profitable is sowing social, cultural, and political division. Its participants are a very tiny, skewed slice of humanity that has American journalism in a choke hold. Twitter does not operate on the principle of representation, which is the cornerstone of democratic governance. It has no concept of the “civil” in “civil society.” Nor has Elon Musk, at any point in his career, displayed any commitment to either democratic governance or the freedom of expression.
Musk gave Isaacson a different explanation for buying the company: “Unless the woke-mind virus, which is fundamentally antiscience, antimerit, and antihuman in general, is stopped, civilization will never become multiplanetary.” It’s as if Musk had come to believe the sorts of mission statements that the man-boy gods of Silicon Valley had long been peddling. “At first, I thought it didn’t fit into my primary large missions,” he told Isaacson, about Twitter. “But I’ve come to believe it can be part of the mission of preserving civilization, buying our society more time to become multiplanetary.”
Elon Musk plans to make the world safe for democracy, save civilization from itself, and bring the light of human consciousness to the stars in a ship he will call the Heart of Gold, for a spaceship fuelled by an Improbability Drive in “The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy.” In case you’ve never read it, what actually happens in “The Hitchhiker’s Guide” is that the Heart of Gold is stolen by Zaphod Beeblebrox, who is the President of the Galaxy, has two heads and three arms, is the inventor of the Pan Galactic Gargle Blaster, has been named, by “the triple-breasted whore of Eroticon 6,” the “Biggest Bang Since the Big One,” and, according to his private brain-care specialist, Gag Halfrunt, “has personality problems beyond the dreams of analysts.” Person of the Year material, for sure. All the same, as a Vogon Fleet prepares to shoot down the Heart of Gold with Beeblebrox on board, Halfrunt muses that “it will be a pity to lose him,” but, “well, Zaphod’s just this guy, you know?” ♦
New Yorker Favorites
The best performances of 2024.
A professor claimed to be Native American. Did she know she wasn’t ?
Kanye West bought an architectural treasure—then gave it a violent remix .
Why so many people are going “ no contact ” with their parents.
Ina Garten and the age of abundance .
How a homegrown teen gang punctured the image of an upscale community .
Sign up for our daily newsletter to receive the best stories from The New Yorker .

Reading the Best Biographies of All Time

Review of “Elon Musk” by Walter Isaacson
17 Sunday Sep 2023
Posted by Steve in Business
≈ 3 Comments
biographies , book reviews , Elon Musk , SpaceX , Tesla , Walter Isaacson

“ Elon Musk ” is Walter Isaacson’s long-anticipated biography of the mercurial entrepreneur behind SpaceX, Tesla and, most recently, the website formerly known as Twitter. Isaacson is an author, journalist and professor at Tulane University who has written popular biographies of Ben Franklin , Albert Einstein , Steve Jobs and Leonardo da Vinci .
Despite my bias against biographies of people whose lives are still unfolding, Isaacson’s biography of Elon Musk’s life proved irresistibly tempting. I was lured by my experience with two of his previous books, the prospect of gaining insight into Musk’s entrepreneurial magic and by the possibility of understanding what makes this volatile visionary tick .
But for all the potential this biography seems to offer – the world’s richest man allowed Isaacson to shadow him for more than two years – the 615-page narrative leaves me feeling deeply ambivalent. The fact this is not a “traditional” biography is not surprising. Nor is Isaacson’s attraction to a controversial figure like Musk. But the fact this biography often reads like a breezy, over-simplified exposè is decidedly disappointing.
Readers hoping to encounter a dispassionate examination of Musk’s strengths and weaknesses will be disappointed. Rather than exploring his subject’s most notorious flaws within the context of his trailblazing successes, Isaacson seems to have lost himself in the hyper-reality bubble surrounding Musk. A biographer is normally expected to be an impartial observer reporting history without leaving footprints, but Isaacson’s role here seems to have evolved into part-time friend, confidante and therapist.
While guiding the reader through Musk’s various achievements, near-misses and interpersonal schisms, Isaacson often refers back to one of his earlier biographical subjects: Steve Jobs. These comparisons, along with accounts of Musk’s relationships with Jeff Bezos, Bill Gates and other successful entrepreneurs and investors, are quite interesting. But Isaacson avoids the real work of digging deeply to determine whether Musk’s frequently callous treatment of people is a requirement for his success…or an unfortunate byproduct of his creative disruption.
And while Isaacson diligently documents much of the individual damage resulting from Musk’s impetuous behavior, he almost completely ignores alleged larger-scale issues such as an apparent disregard for highway traffic safety laws, widespread allegations of consumer fraud, a tolerance of toxic behavior on his social networking site and a disregard for laws designed to ensure financial market transparency and fairness.
Finally, Isaacson’s writing style is unusually informal and lacks an eloquent literary voice. His narrative is essentially a stitched-together collection of reminiscences, clichés and revealing fly-on-the-wall observations which seems to have been designed for fast, effortless consumption by the reader.
In spite of its flaws there is much to enjoy in this dissection of Musks’s conspicuously captivating life. Isaacson does a nice job reviewing Musk’s troubled childhood, his turbulent relationship with his father (whose own list of foibles is remarkable) and his inability to foster healthy long-term relationships. And the list of people Isaacson convinced to speak “on the record” is impressive.
Musk’s persistent desire to challenge conventional wisdom in the face of long odds and entrenched interests is a recurring theme and Isaacson never misses an opportunity to demonstrate Musk’s intuitive sense for when and where to test boundaries and spark long-needed change. This window into Musk’s relentless drive, particularly in the electric vehicle and space industries, may be the most compelling aspect of the book.
In addition, although the narrative proves far too casual and carefree for literary connoisseurs, one of its strengths is undoubtedly its accessibility. No reader will get lost in a maze of confusing engineering syntax, complex financial jargon or tedious corporate history. Isaacson clearly intended this book to provide its audience with an easy, uncluttered reading experience. One thing is certain: “Elon Musk” is never dull.
Overall, Walter Isaacson’s hot-off-the-press biography provides readers with a fast-paced, interesting and revealing look at Elon Musk – the genius and the jerk . But the book’s shortcomings are conspicuous and Isaacson’s proximity to his subject, and his willingness to rationalize or excuse Musk’s most profound flaws, limit this book’s efficacy as a biography.
Overall rating: 3 stars
3 thoughts on “Review of “Elon Musk” by Walter Isaacson”
September 17, 2023 at 10:33 pm
Huzzah. You are back to writing and providing your excellent Biographical reviews. Looking forward to your comments on Richard Norton Smith’s book on Gerald Ford.
September 21, 2023 at 10:34 am
I like the book not so much the subject. The technology aspects of his story are very interesting. So yup Musk is a smart guy with a sick work ethic who has been smart enough to surround himself with brilliant people. So, yes all that is admirable. But that’s where the admiration stops.
The human carnage along the way leaves very little to admire. Musk was reported to berate a male employee who missed a Tesla event to be present for the birth of his child. He’s been married 5 times (twice to the same woman) and has had multiple relationships. The book relates a story about him discussing and thinking about how to fit a new relationship into his schedule. He reportedly commented, “How much time does a woman want a week? Maybe 10 hours?”
His 7 children from multiple relationships have nannies and a nanny manager. In addition to traditional names for some of his children, he has two children named “X AE A-XIIHe” and “Exa Dark Sideræl Musk” respectively. So yup not only is he weird he’s saddled infants with wacky names cuz he thinks it’s cool. Wow. He rents castles and sumo wrestlers for his parties. So if you’re into the weird and wacky, he’s your guy.
September 30, 2023 at 6:33 pm
3 stars: Not enough elonbad.
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
- ADMIN AREA MY BOOKSHELF MY DASHBOARD MY PROFILE SIGN OUT SIGN IN
Awards & Accolades
Our Verdict
Kirkus Reviews' Best Books Of 2023
New York Times Bestseller

by Walter Isaacson ‧ RELEASE DATE: Sept. 12, 2023
Alternately admiring and critical, unvarnished, and a closely detailed account of a troubled innovator.
A warts-and-all portrait of the famed techno-entrepreneur—and the warts are nearly beyond counting.
To call Elon Musk (b. 1971) “mercurial” is to undervalue the term; to call him a genius is incorrect. Instead, Musk has a gift for leveraging the genius of others in order to make things work. When they don’t, writes eminent biographer Isaacson, it’s because the notoriously headstrong Musk is so sure of himself that he charges ahead against the advice of others: “He does not like to share power.” In this sharp-edged biography, the author likens Musk to an earlier biographical subject, Steve Jobs. Given Musk’s recent political turn, born of the me-first libertarianism of the very rich, however, Henry Ford also comes to mind. What emerges clearly is that Musk, who may or may not have Asperger’s syndrome (“Empathy did not come naturally”), has nurtured several obsessions for years, apart from a passion for the letter X as both a brand and personal name. He firmly believes that “all requirements should be treated as recommendations”; that it is his destiny to make humankind a multi-planetary civilization through innovations in space travel; that government is generally an impediment and that “the thought police are gaining power”; and that “a maniacal sense of urgency” should guide his businesses. That need for speed has led to undeniable successes in beating schedules and competitors, but it has also wrought disaster: One of the most telling anecdotes in the book concerns Musk’s “demon mode” order to relocate thousands of Twitter servers from Sacramento to Portland at breakneck speed, which trashed big parts of the system for months. To judge by Isaacson’s account, that may have been by design, for Musk’s idea of creative destruction seems to mean mostly chaos.
Pub Date: Sept. 12, 2023
ISBN: 9781982181284
Page Count: 688
Publisher: Simon & Schuster
Review Posted Online: Sept. 12, 2023
Kirkus Reviews Issue: Oct. 15, 2023
BIOGRAPHY & MEMOIR | SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY | BUSINESS | POLITICS | ISSUES & CONTROVERSIES | GENERAL BIOGRAPHY & MEMOIR
Share your opinion of this book
More by Walter Isaacson

BOOK REVIEW
by Walter Isaacson with adapted by Sarah Durand

by Walter Isaacson

More About This Book

BOOK TO SCREEN

by Stephanie Johnson & Brandon Stanton illustrated by Henry Sene Yee ‧ RELEASE DATE: July 12, 2022
A blissfully vicarious, heartfelt glimpse into the life of a Manhattan burlesque dancer.
A former New York City dancer reflects on her zesty heyday in the 1970s.
Discovered on a Manhattan street in 2020 and introduced on Stanton’s Humans of New York Instagram page, Johnson, then 76, shares her dynamic history as a “fiercely independent” Black burlesque dancer who used the stage name Tanqueray and became a celebrated fixture in midtown adult theaters. “I was the only black girl making white girl money,” she boasts, telling a vibrant story about sex and struggle in a bygone era. Frank and unapologetic, Johnson vividly captures aspects of her former life as a stage seductress shimmying to blues tracks during 18-minute sets or sewing lingerie for plus-sized dancers. Though her work was far from the Broadway shows she dreamed about, it eventually became all about the nightly hustle to simply survive. Her anecdotes are humorous, heartfelt, and supremely captivating, recounted with the passion of a true survivor and the acerbic wit of a weathered, street-wise New Yorker. She shares stories of growing up in an abusive household in Albany in the 1940s, a teenage pregnancy, and prison time for robbery as nonchalantly as she recalls selling rhinestone G-strings to prostitutes to make them sparkle in the headlights of passing cars. Complemented by an array of revealing personal photographs, the narrative alternates between heartfelt nostalgia about the seedier side of Manhattan’s go-go scene and funny quips about her unconventional stage performances. Encounters with a variety of hardworking dancers, drag queens, and pimps, plus an account of the complexities of a first love with a drug-addled hustler, fill out the memoir with personality and candor. With a narrative assist from Stanton, the result is a consistently titillating and often moving story of human struggle as well as an insider glimpse into the days when Times Square was considered the Big Apple’s gloriously unpolished underbelly. The book also includes Yee’s lush watercolor illustrations.
Pub Date: July 12, 2022
ISBN: 978-1-250-27827-2
Page Count: 192
Publisher: St. Martin's
Review Posted Online: July 27, 2022
BIOGRAPHY & MEMOIR | ENTERTAINMENT, SPORTS & CELEBRITY | GENERAL BIOGRAPHY & MEMOIR
More by Brandon Stanton

by Brandon Stanton

by Brandon Stanton photographed by Brandon Stanton

by Brandon Stanton ; photographed by Brandon Stanton

by Melania Trump ‧ RELEASE DATE: Oct. 8, 2024
A slick, vacuous glimpse into the former first lady’s White House years.
A carefully curated personal portrait.
First ladies’ roles have evolved significantly in recent decades. Their memoirs typically reflect a spectrum of ambition and interests, offering insights into their values and personal lives. Melania Trump, however, stands out as exceptionally private and elusive. Her ultra-lean account attempts to shed light on her public duties, initiatives, and causes as first lady, and it defends certain actions like her controversial “I REALLY DON’T CARE, DO U?” jacket. The statement was directed at the media, not the border situation, she claims. Yet the book provides scant detail about her personal orbit or day-to-day interactions. The memoir opens with her well-known Slovenian origin story, successful modeling career, and whirlwind romance with Donald Trump, culminating in their 2005 marriage, followed by a snapshot of Election Day 2016: “Each time we were together that day, I was impressed by his calm.…This man is remarkably confident under pressure.” Once in the White House, Melania Trump describes her functions and numerous public events at home and abroad, which she asserts were more accomplished than media representations suggested. However, she rarely shares any personal interactions beyond close family ties, notably her affection for her son, Barron, and her sister, Ines. And of course she lavishes praise on her husband. Minimal anecdotes about White House or cabinet staff are included, and she carefully defuses her rumored tensions with Trump’s adult children, blandly stating, “While we may share the same last name, each of us is distinct with our own aspirations and paths to follow.” Although Melania’s desire to support causes related to children’s and women’s welfare feels authentic, the overall tenor of her memoir seems aimed at painting a glimmering portrait of her husband and her role, likely with an eye toward the forthcoming election.
Pub Date: Oct. 8, 2024
ISBN: 9781510782693
Page Count: 256
Publisher: Skyhorse Publishing
Review Posted Online: Oct. 14, 2024
Kirkus Reviews Issue: Dec. 1, 2024
BIOGRAPHY & MEMOIR | POLITICAL & ROYALTY | GENERAL BIOGRAPHY & MEMOIR

PERSPECTIVES
- Discover Books Fiction Thriller & Suspense Mystery & Detective Romance Science Fiction & Fantasy Nonfiction Biography & Memoir Teens & Young Adult Children's
- News & Features Bestsellers Book Lists Profiles Perspectives Awards Seen & Heard Book to Screen Kirkus TV videos In the News
- Kirkus Prize Winners & Finalists About the Kirkus Prize Kirkus Prize Judges
- Magazine Current Issue All Issues Manage My Subscription Subscribe
- Writers’ Center Hire a Professional Book Editor Get Your Book Reviewed Advertise Your Book Launch a Pro Connect Author Page Learn About The Book Industry
- More Kirkus Diversity Collections Kirkus Pro Connect My Account/Login
- About Kirkus History Our Team Contest FAQ Press Center Info For Publishers
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Reprints, Permission & Excerpting Policy
© Copyright 2024 Kirkus Media LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Popular in this Genre
Hey there, book lover.
We’re glad you found a book that interests you!
Please select an existing bookshelf
Create a new bookshelf.
We can’t wait for you to join Kirkus!
Please sign up to continue.
It’s free and takes less than 10 seconds!
Already have an account? Log in.
Trouble signing in? Retrieve credentials.
Almost there!
- Industry Professional
Welcome Back!
Sign in using your Kirkus account
Contact us: 1-800-316-9361 or email [email protected].
Don’t fret. We’ll find you.
Magazine Subscribers ( How to Find Your Reader Number )
If You’ve Purchased Author Services
Don’t have an account yet? Sign Up.

IMAGES